According to a study published by the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, early patient mobility significantly improves patient outcomes. In the study, Dale M. Needham, M.D., Ph.D., the university’s lead researcher, notes that patients who spend less time in bed and start rehabilitation sooner are less likely to suffer from muscle weakness, physical impairments, or mental illness than those who do not. Another study published by the National Institutes of Health revealed that patients who spend less time in their hospital beds are also less likely to suffer from the following:
- Pressure ulcers (bedsores)
- Blood clots
- Pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
While we could easily say that these health problems can be avoided by not spending less time in bed, we must also acknowledge that getting out of one’s bed and engaging in physical activity doesn’t come easy for some hospital patients.
Why Some Hospital Patients Are Bedridden
All hospitals are acutely aware of the issues that stem from allowing patients to stay in bed too long. But not all of them have a safe patient handling program that makes it easy for patients with neurological conditions, infections, and vitamin deficiencies, all of which can cause muscle weakness, to get out of bed when they want to or even have to for medical reasons. The same can be said of many other health problems as well.
What Hospitals Are Doing to Promote Early Patient Mobility
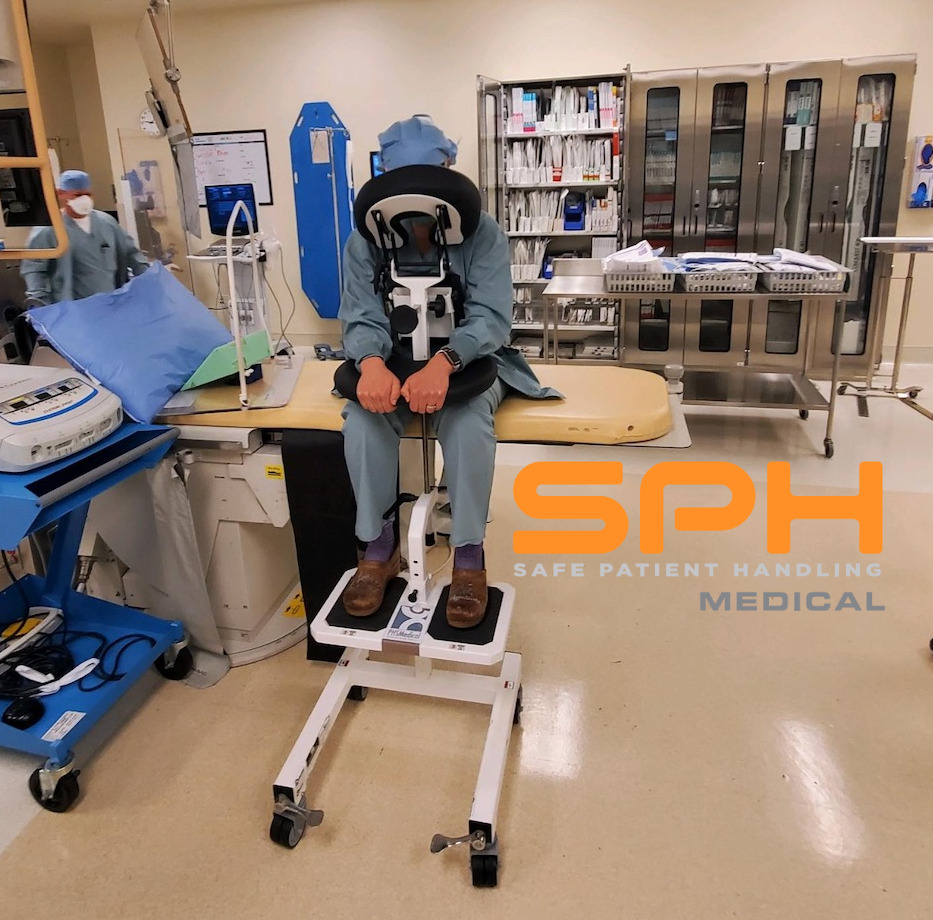
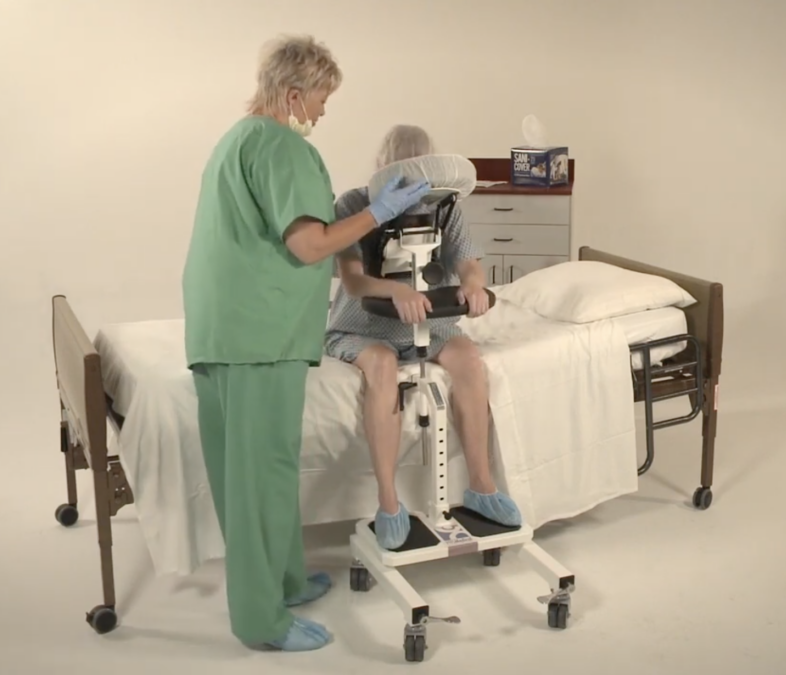
To promote early patient mobility and, as a byproduct of doing so, minimize the risk of many health problems correlated with being bedridden for too long, a lot of hospitals employ safe patient handling programs to ambulate patients. These programs consist of trained medical teams and assistive mobility devices that help get patients moving. And this could mean lifting, repositioning, or transferring them from one department to another. Likewise, it could mean getting them out of bed to exercise so they can avoid many of the health problems mentioned earlier in this article. And it does not end there; several evidence based studies show the combination of highly trained medical teams and assistive mobility devices can also offer the following benefits to long-term hospital patients:
- Improved cardiac function
- Improved muscle mass
- Improved respiratory function
- Minimizing the risk of delirium commonly associated with being bedridden
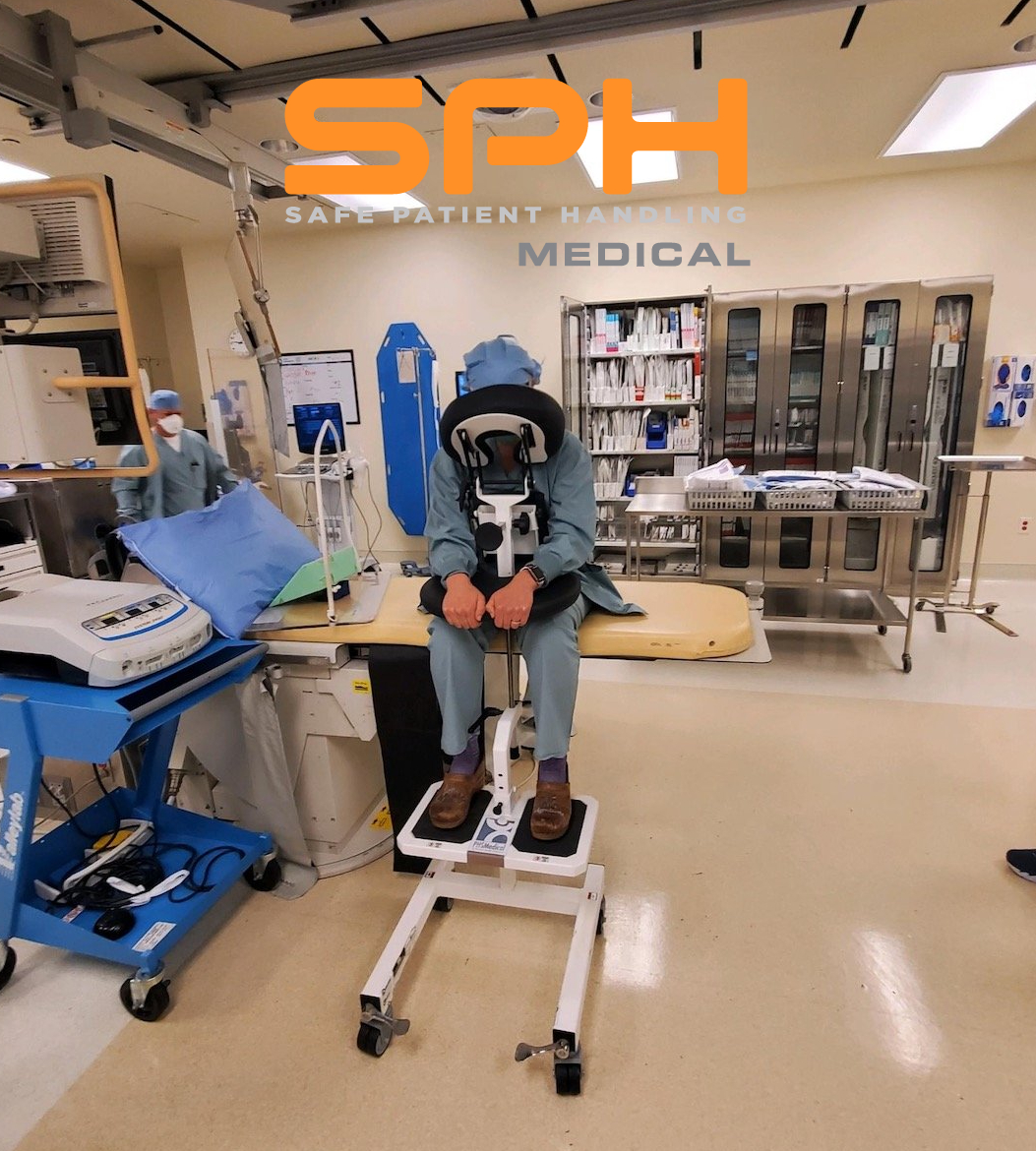
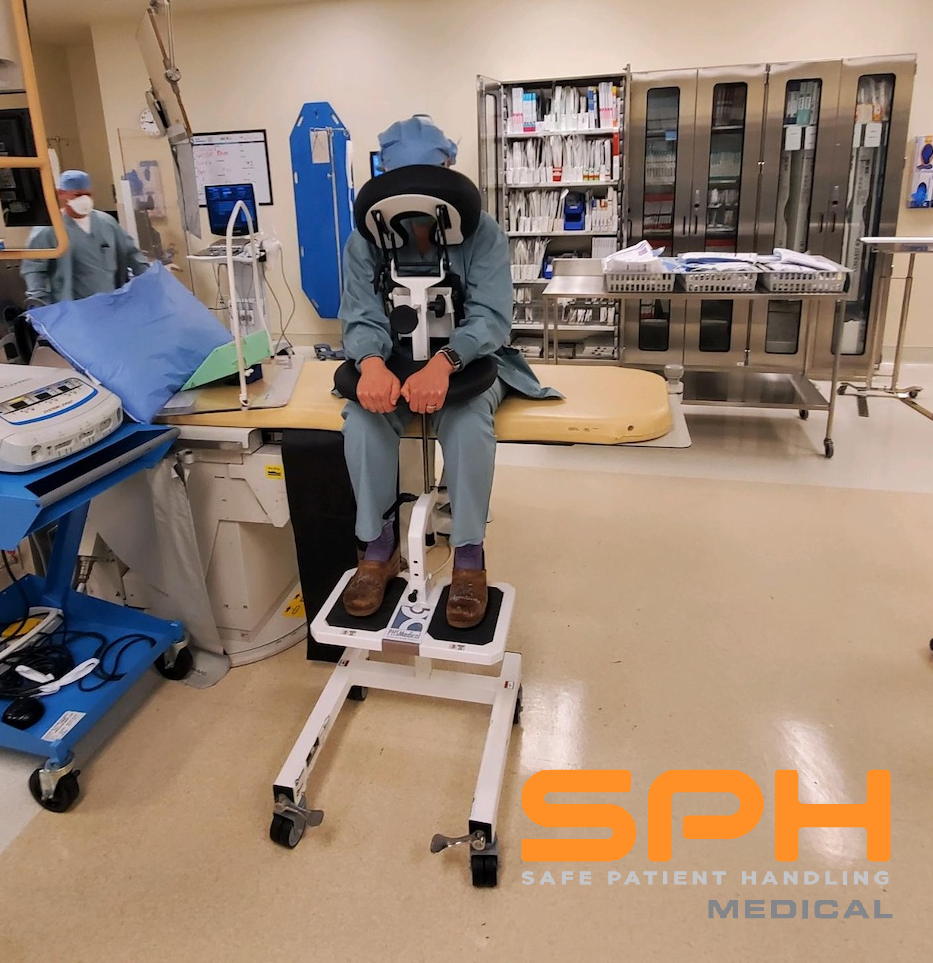
Why Many Hospitals Are Choosing the SPH Medical Rowalker
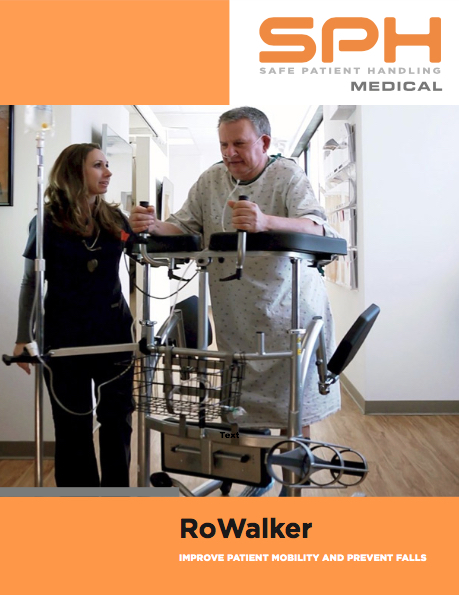
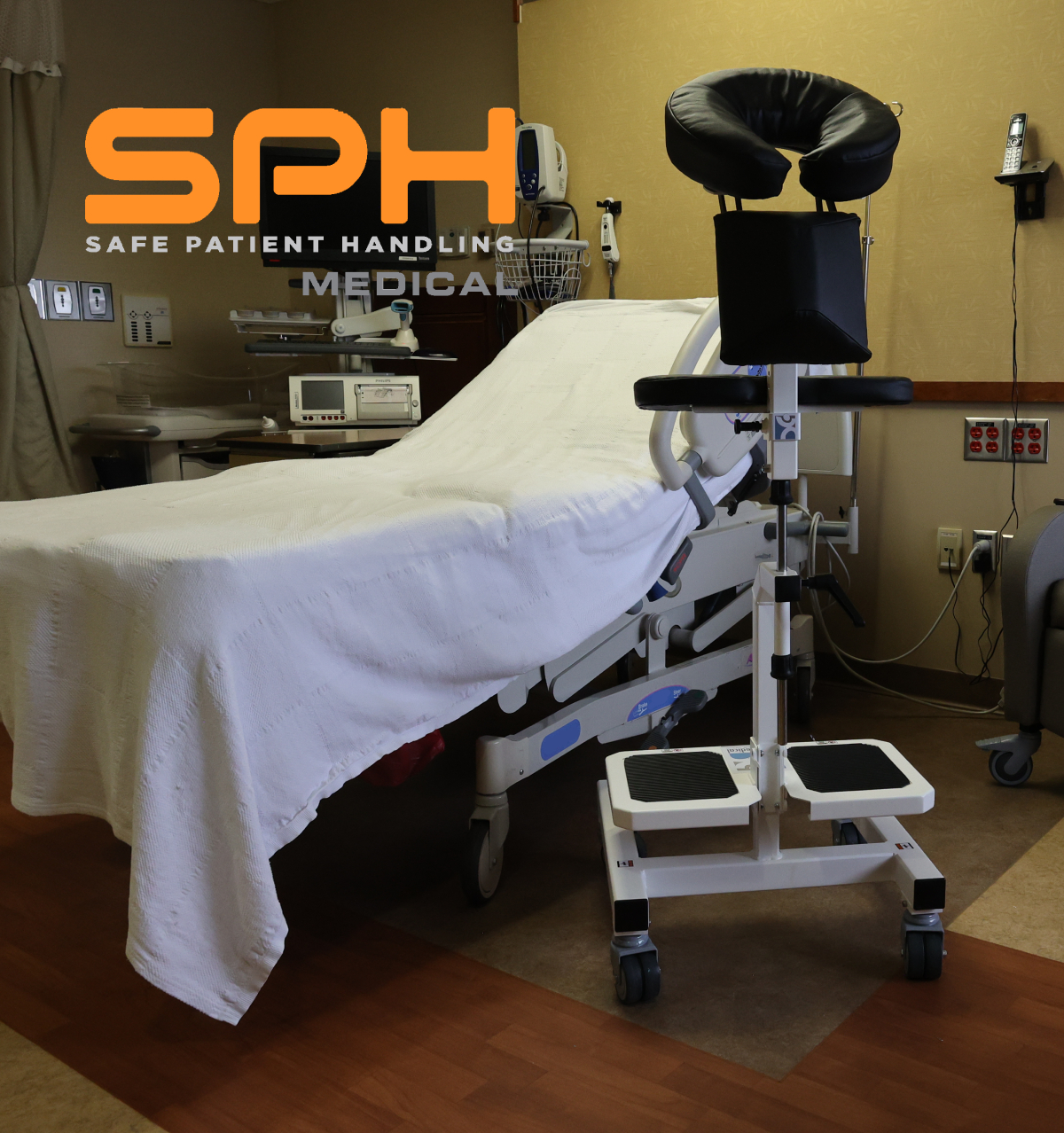
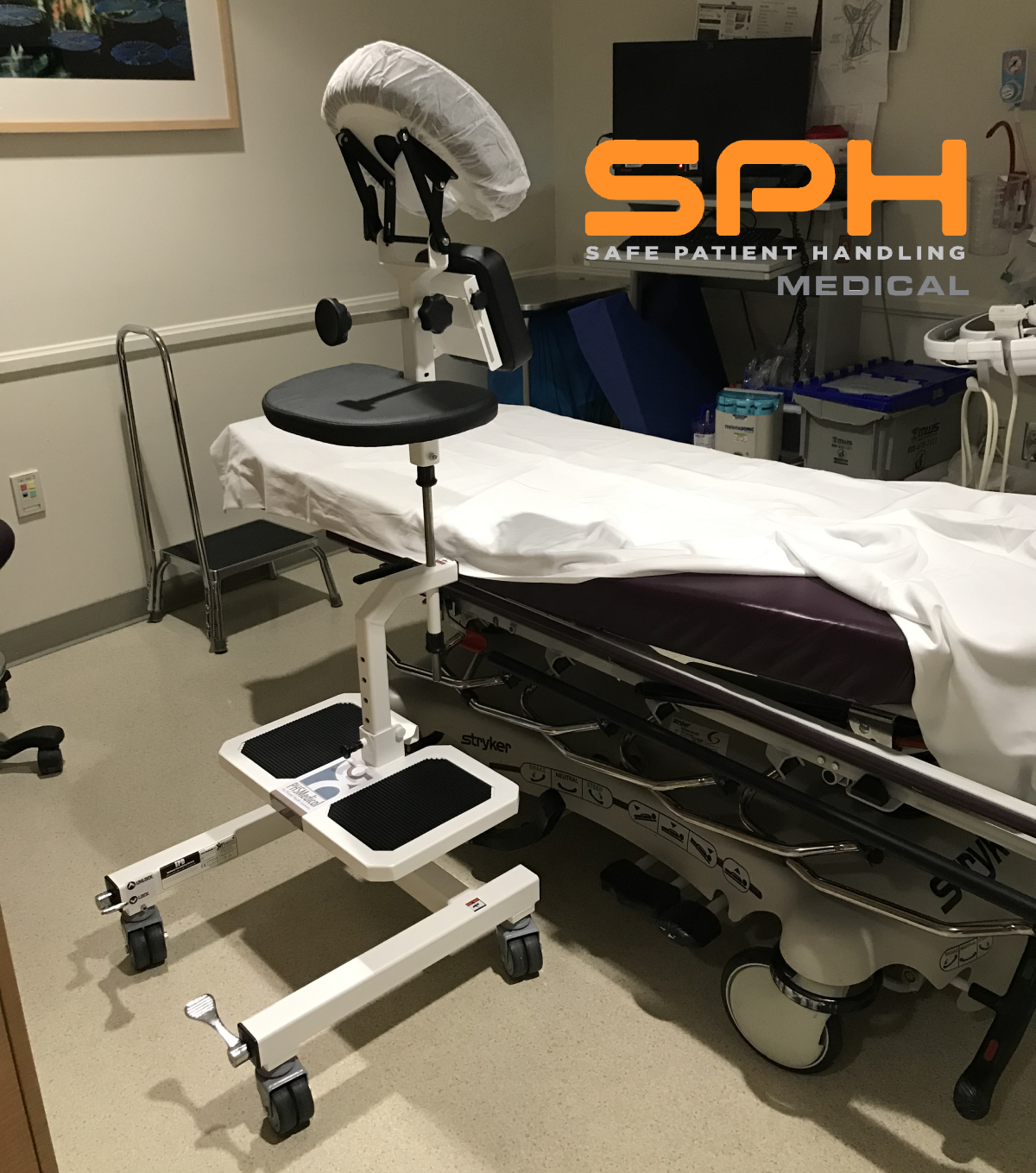
There are many devices that hospitals can use to ambulate patients, but many are choosing to go with the SPH Medical Rowalker. Along with getting patients up and moving, these devices can carry just about everything they might need while in a hospital. Also referred to as an ambulation device or a platform walker, the SPH Medical Rowalker is capable of carrying the following:
- An oxygen tank
- An IV pole
- A cardiac monitor
- A portable ventilator
Early Patient Mobility, The Bottom Line
Because they help patients stand, walk, and feel a little more independent, it is easy to see why many hospitals have made the Rowalker by SPH Medical their ambulation device of choice. Of course, the ability of these devices to lower a patient’s chances of developing blood clots, UTIs, pneumonia, and much more is just icing on the proverbial cake. To learn more about the Rowalker by SPH Medical, consider speaking with one of our associates today.