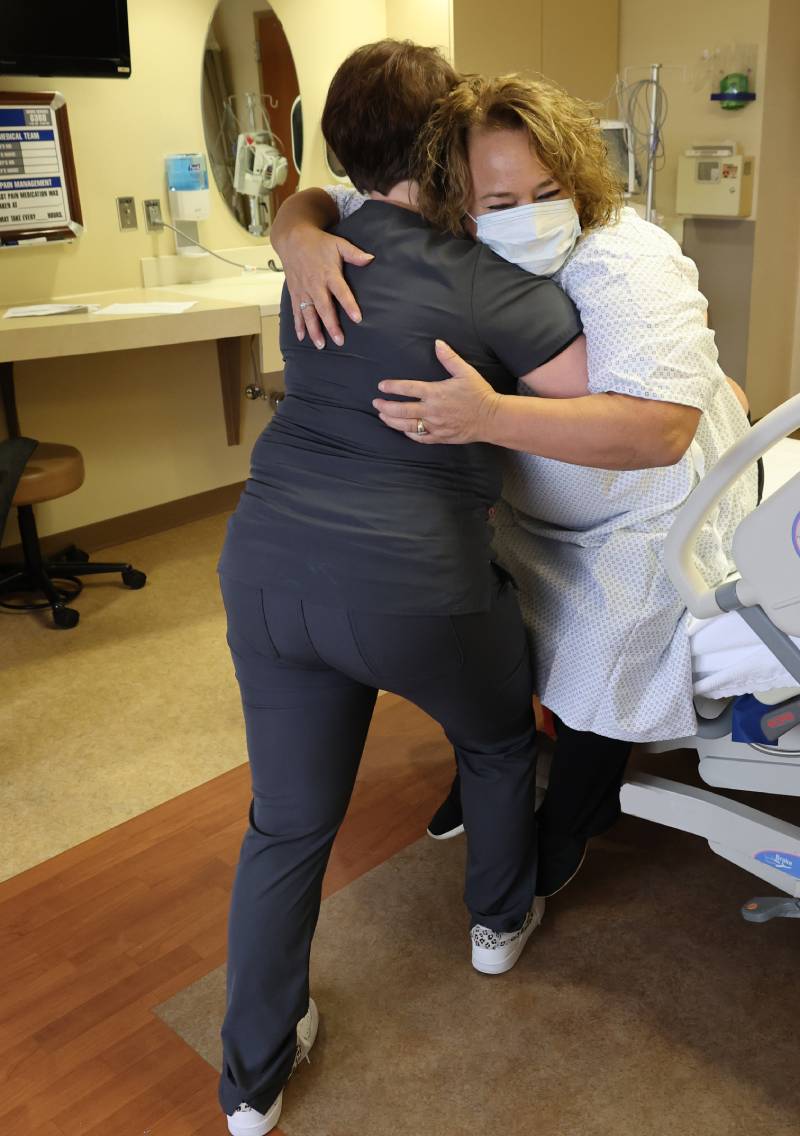
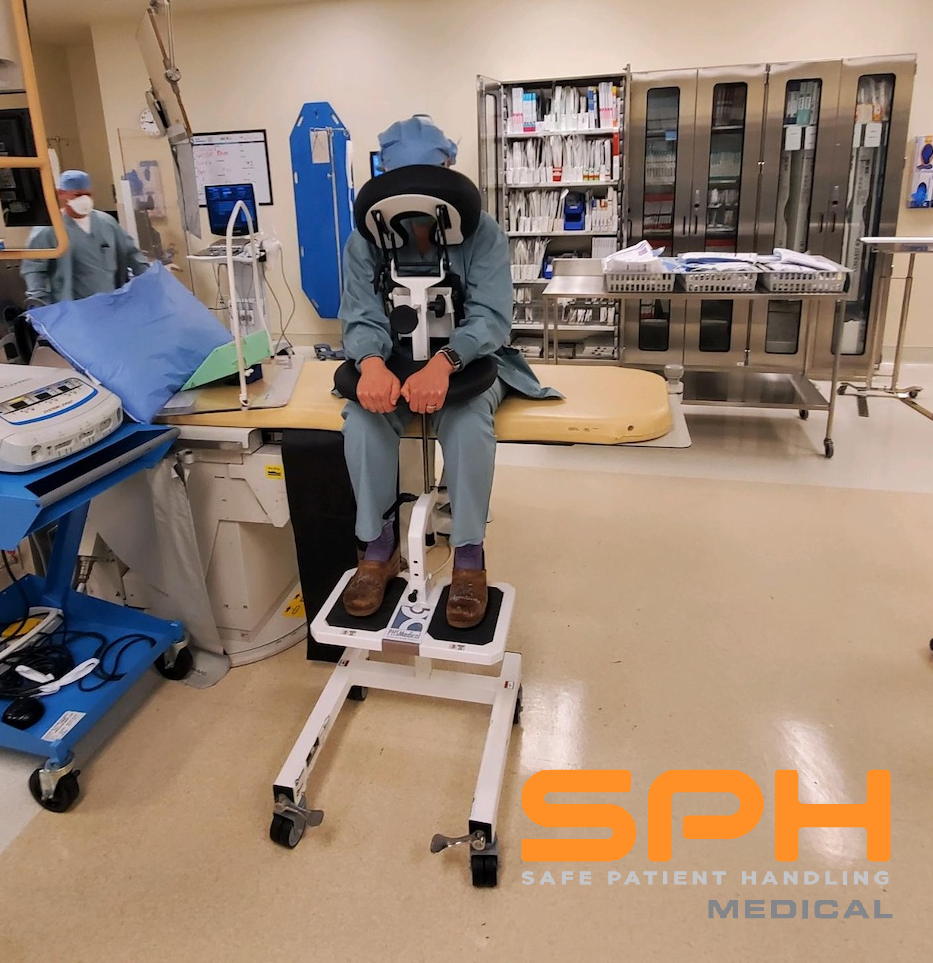
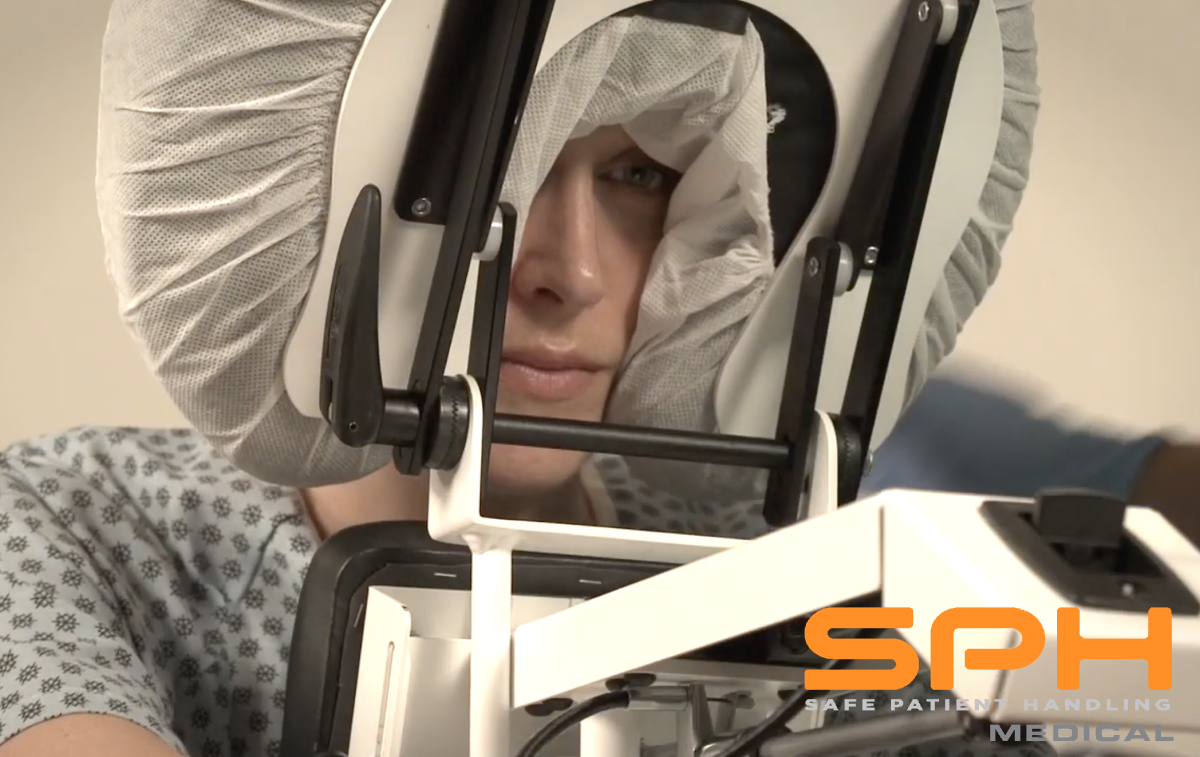
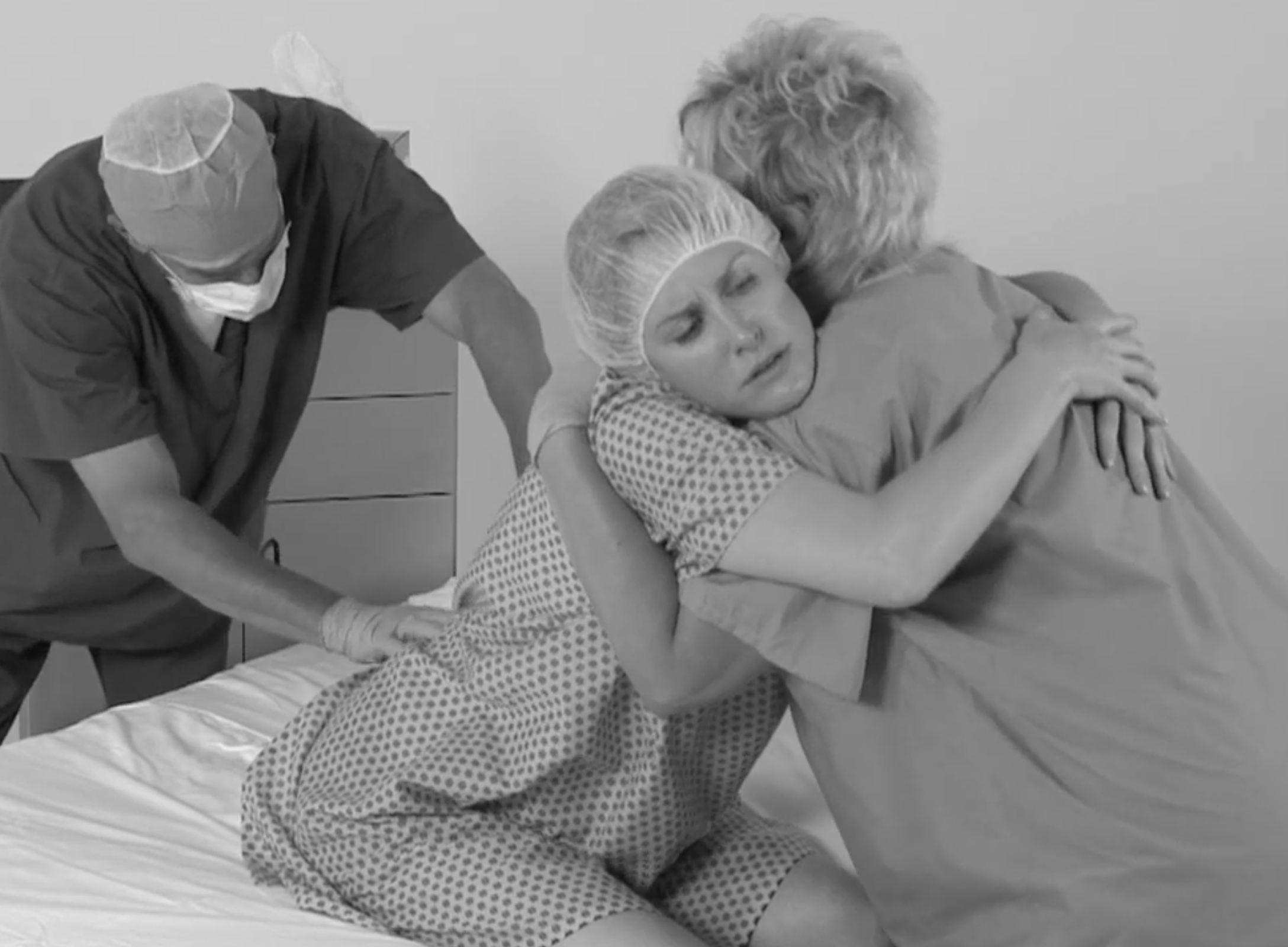
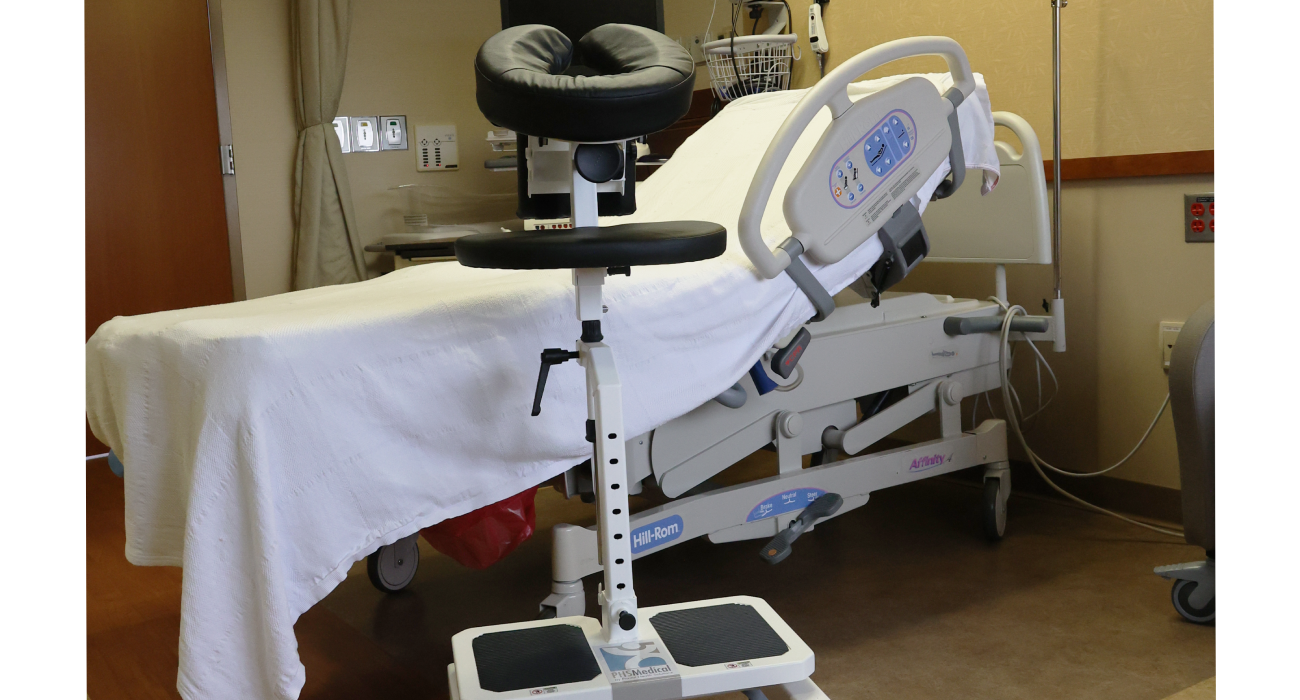
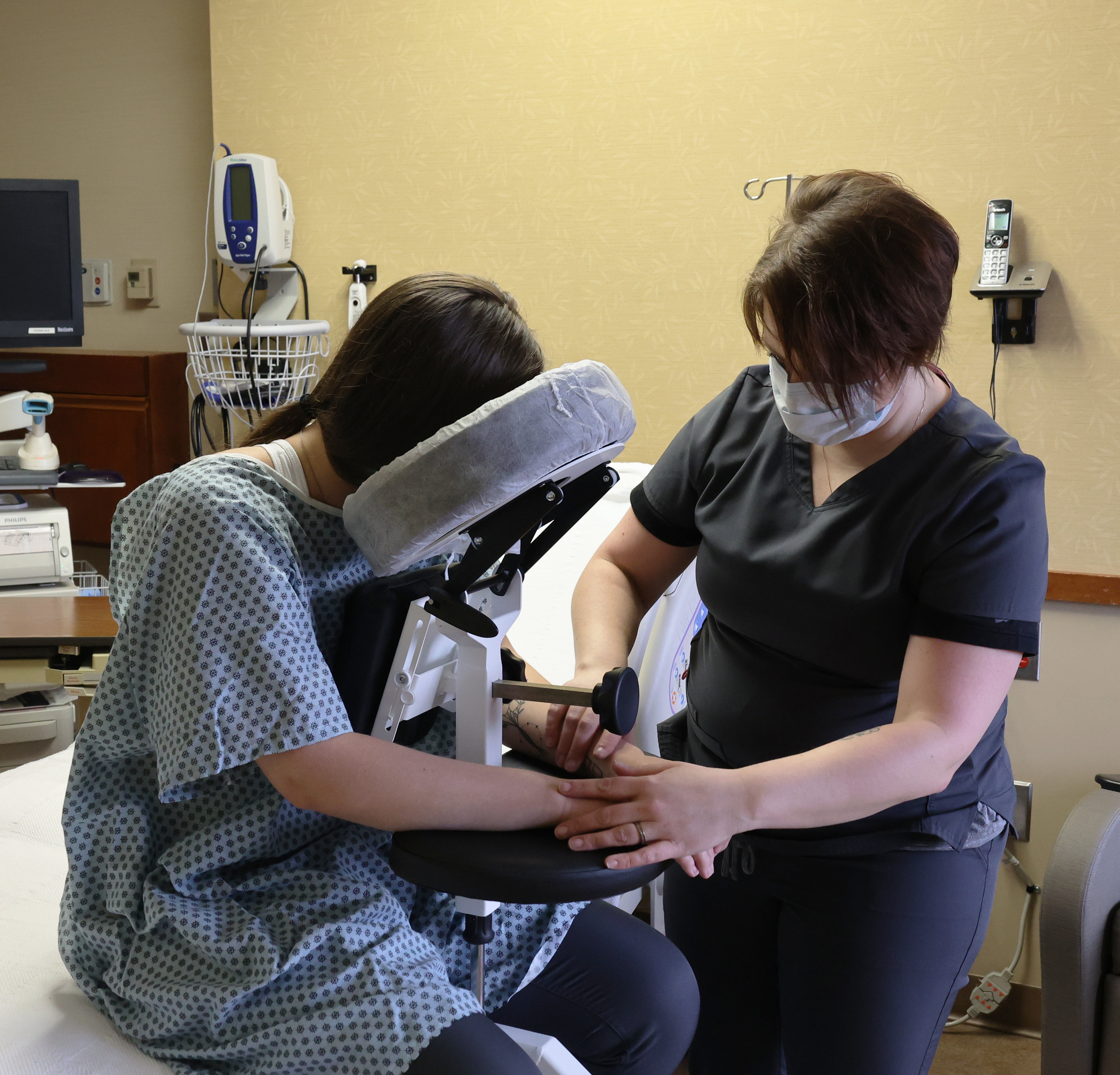
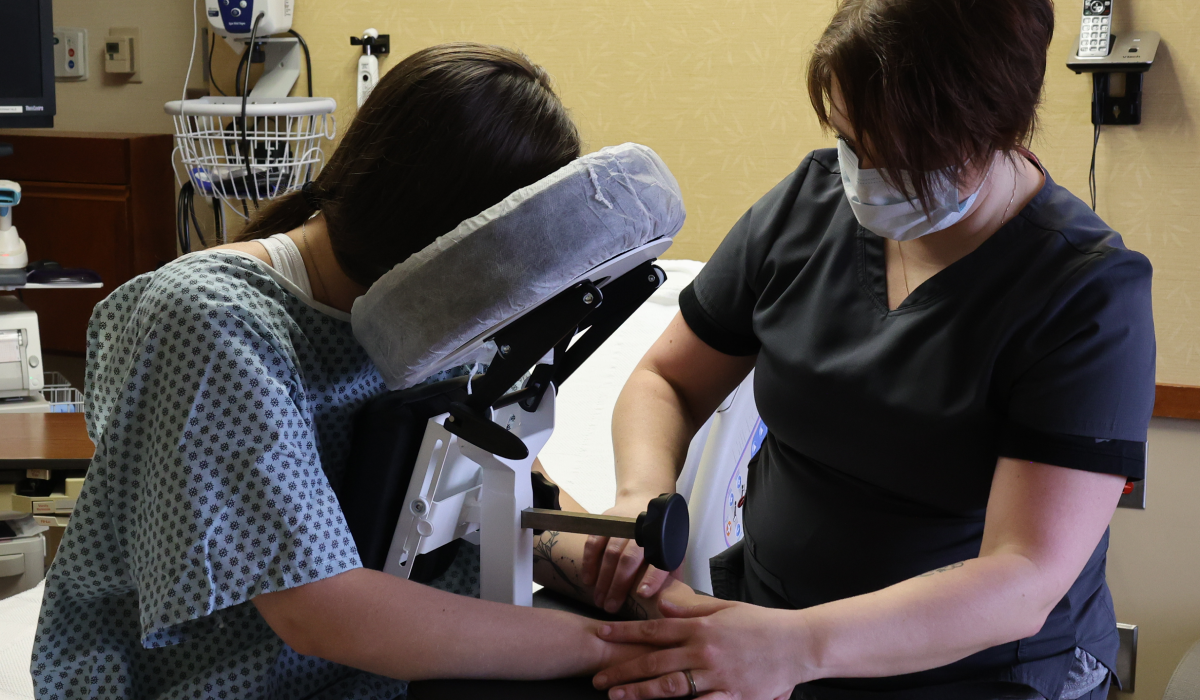
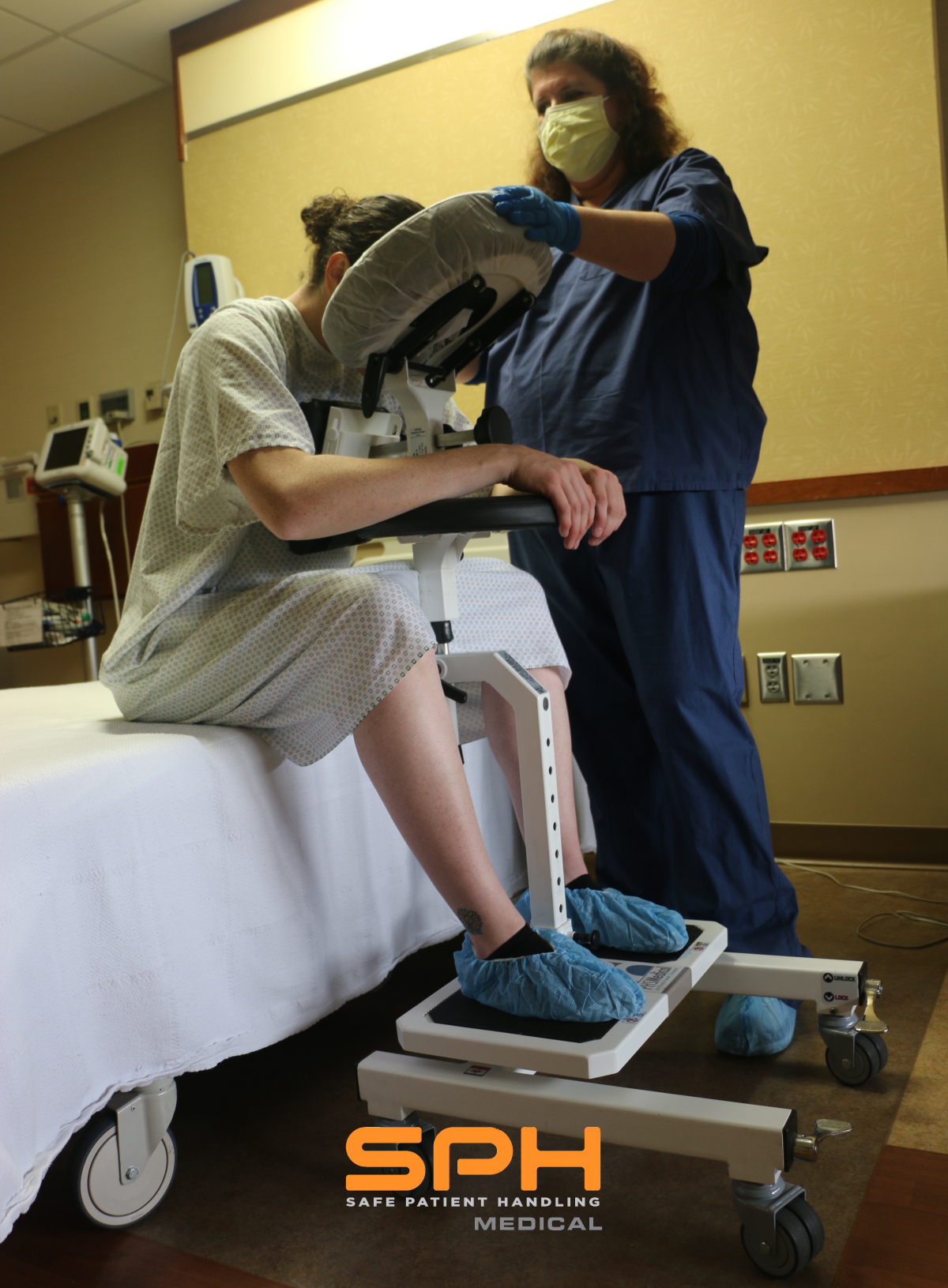
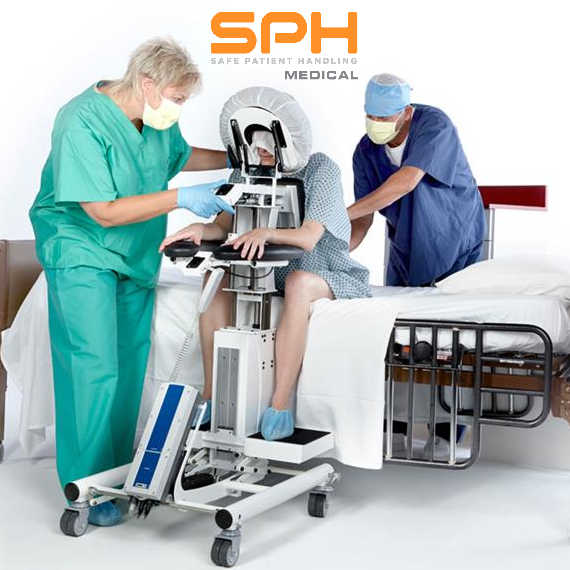
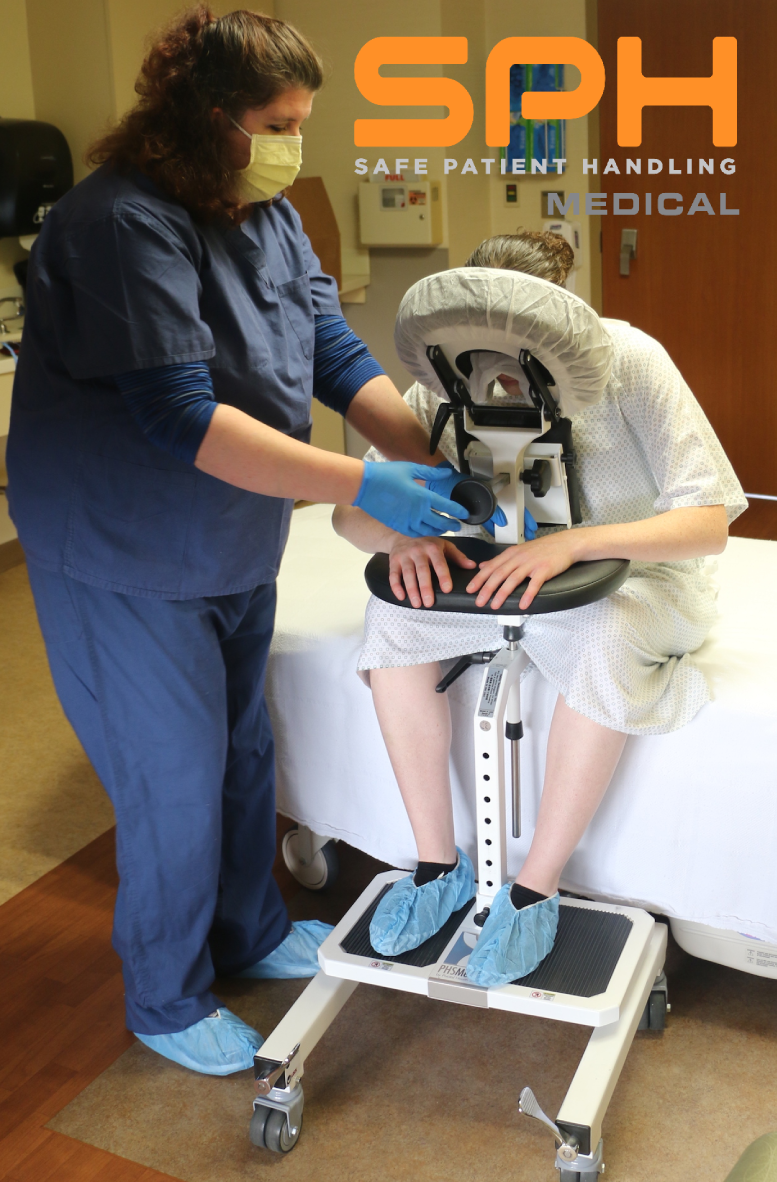
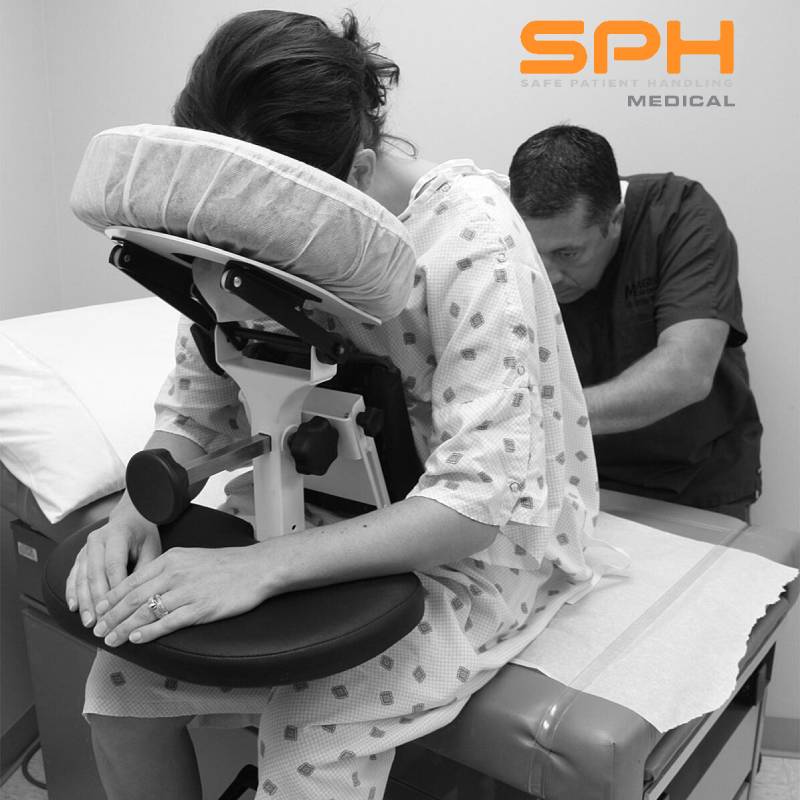
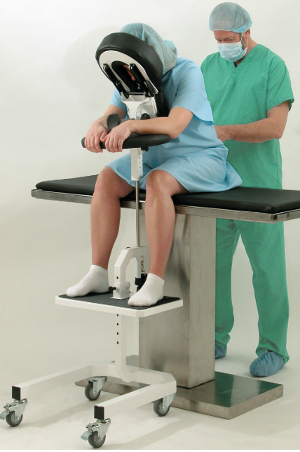
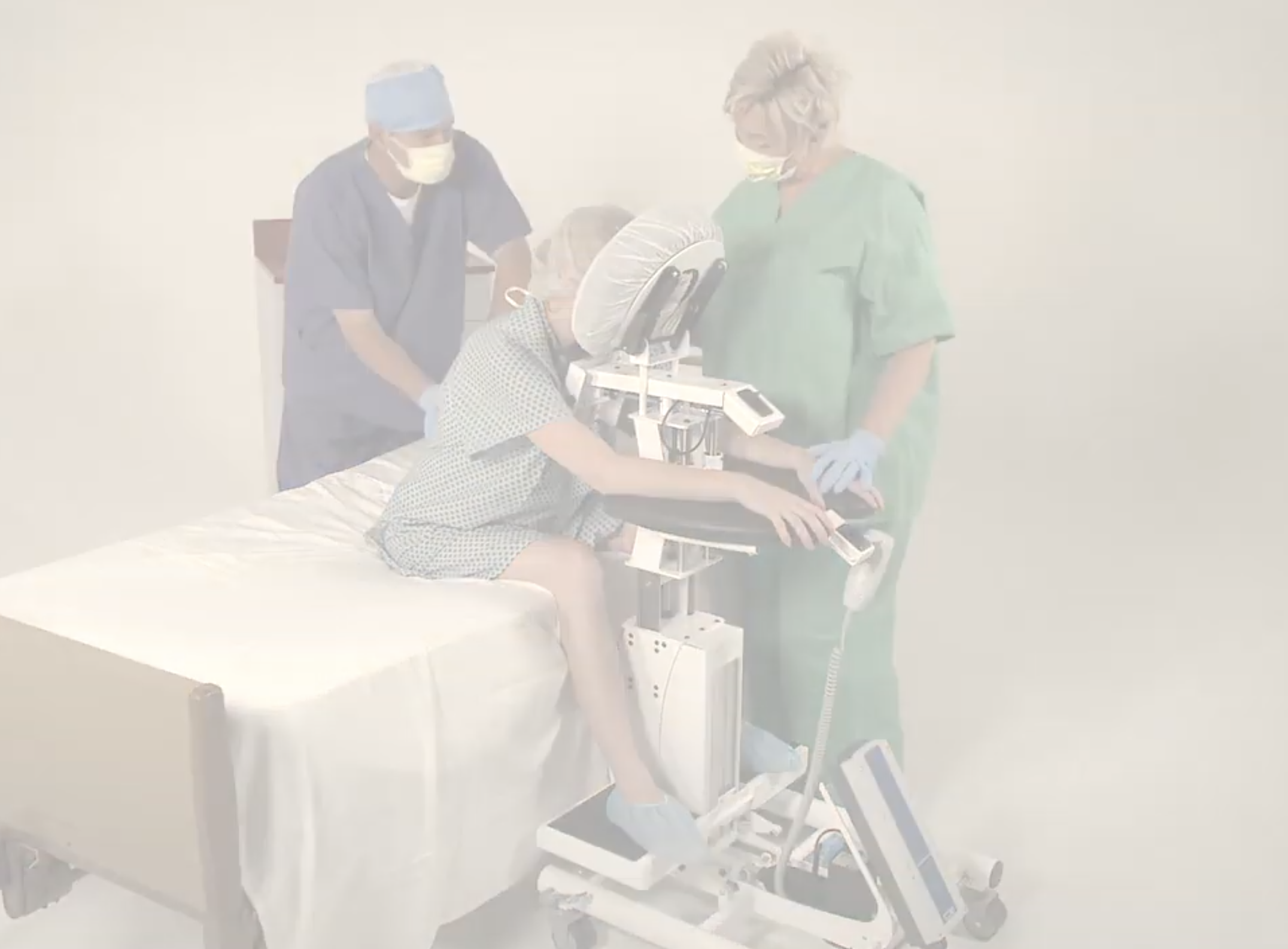
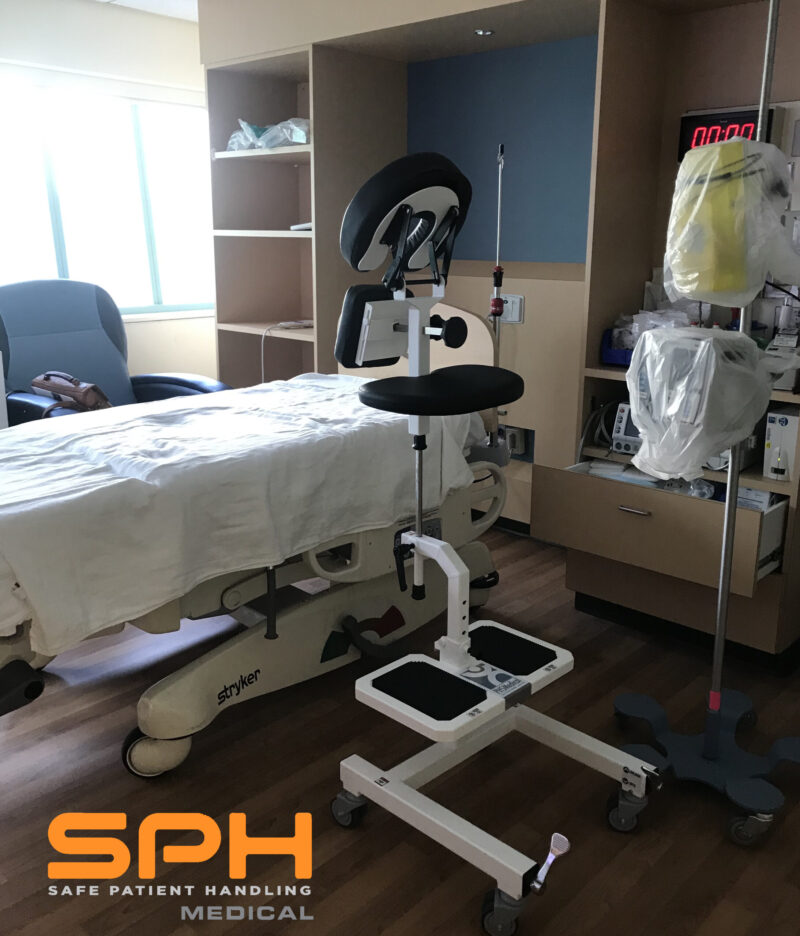
SPH Medical’s Epidural Positioning Device (EPD) is a breakthrough tool that is transforming the landscape of imaging and interventional radiology departments across the nation. The device’s innovative design and functionality make it an invaluable asset in these departments, where precision, patient comfort, and safety are paramount. With Interventional Radiology and EPD, or Epidural Chair, this is quickly becoming a standard of care at leading healthcare facilities in multiple departments to solve patient positioning challenges that put staff at risk of a musculoskeletal injury.
A Deep Dive: Upright Seated Procedures in Interventional Radiology and EPD
Interventional radiology and imaging departments are often the unseen heroes of medical diagnostics and treatment. Among the myriad procedures they handle, thoracentesis stands out as a procedure that requires the patient to be in an upright seated position, making it a perfect candidate for the benefits offered by the EPD.
Thoracentesis: A Closer Look
Thoracentesis is a minimally invasive procedure performed to remove excess fluid from the space between the lungs and the chest wall, known as the pleural space. This excess fluid, if not treated, can cause shortness of breath or even lead to serious complications like pneumonia or lung collapse.
During thoracentesis, the patient is typically seated upright with their arms resting on a table. This position allows healthcare providers to access the pleural space more easily. However, maintaining this position can be challenging and uncomfortable for patients, especially those with chronic conditions or limited mobility.
The Integral Role of the EPD in Imaging and Interventional Radiology
In the world of imaging and interventional radiology, the EPD plays a pivotal role by facilitating precise patient positioning for various procedures. This precise positioning is crucial for obtaining high-quality images, which in turn, aids in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Moreover, the EPD significantly enhances patient comfort and safety during interventional radiology procedures. Its ergonomic design supports the patient’s body, allowing them to maintain the required position for extended periods without discomfort. This focus on patient comfort not only improves the patient experience but also reduces the risk of movement-related complications during procedures.
Interventional Radiology and EPD; The Unsurpassed Benefits
The benefits of the EPD extend beyond patient comfort and safety. It contributes significantly to reducing the risk of complications associated with poor positioning, such as suboptimal image quality or procedural difficulties. With the EPD, healthcare professionals can obtain clearer images, leading to more accurate diagnoses and more effective interventions.
Additionally, the EPD offers substantial advantages for healthcare providers. Its design reduces physical strain on radiologists and technicians, who no longer need to manually adjust patients during procedures. This ergonomic advantage can lessen the occurrence of work-related injuries among medical staff, enhancing overall department efficiency.
Proven Effectiveness: Case Studies and Statistics
The effectiveness of the EPD isn’t merely theoretical; it’s supported by real-world examples and compelling statistics. An increasing number of imaging and interventional radiology departments nationwide are reporting improved patient outcomes and increased staff satisfaction after implementing the EPD in their procedures1.
A Resounding Call to Action
SPH Medical’s Epidural Positioning Device (EPD) is a breakthrough tool that is transforming the landscape of Interventional Radiology and EPD. The device’s innovative design and functionality make it an invaluable asset in these departments, where precision, patient comfort, and safety are paramount.
In light of these undeniable benefits, the conclusion is clear: the EPD from SPH Medical is an essential tool for any imaging or interventional radiology department. Its combination of precision, comfort, safety, and provider-friendly design make it an invaluable asset for enhancing patient care and staff wellbeing. We strongly encourage hospitals and imaging centers nationwide to consider its implementation. Embrace the future of imaging and interventional radiology care with the Epidural Positioning Device – a decision that promises unparalleled benefits for patients and healthcare providers alike.