According to MedlinePlus, a trusted online resource for up-to-date information related to diseases and a host of wellness issues, a spinal block is commonly prescribed to patients undergoing genital, urinary tract, or other lower body medical procedures. They are also prescribed to pregnant women, in addition to epidural anesthesia, before they are due to give birth in a hospital’s labor and delivery unit. Also known as spinal anesthesia, a spinal block is a type of neuraxial regional anesthesia that involves injecting a local anesthetic or opioid directly into the subarachnoid space to block pain signals that would otherwise travel to the brain. Spinal blocks do a terrific job of keeping pain at bay so that patients can get through a needed medical procedure. But they can sometimes pose a danger to patients and medical teams alike. Improving safety during spinal blocks can be done with an epidural chair or epidural positioning device.
Safety During Spinal Blocks: The Dangers They Pose to Patients and Medical Teams Alike
Studies show that spinal blocks can increase a patient’s chances of experiencing low blood pressure, meningitis or abscess, hematomas, difficulty urinating, seizures, and headaches. As far as medical teams are concerned, many suffer musculoskeletal injuries due to lifting, repositioning, or catching falling patients that have received spinal blocks. Most of these injuries involve back pain and back strain that is so severe that many say they can’t work for a few days following their injury. To further put this into perspective, in 2016, the 8,730 days-away-from-work cases filed by hospitals involved medical teams that suffered musculoskeletal injuries while tending to patients in a hospital’s surgery department or labor and delivery unit. An epidural positioning device (EPD), such as an epidural chair, could have helped medical teams in these hospitals avoid many of these injuries, as well as improve safety during spinal blocks and epidurals.
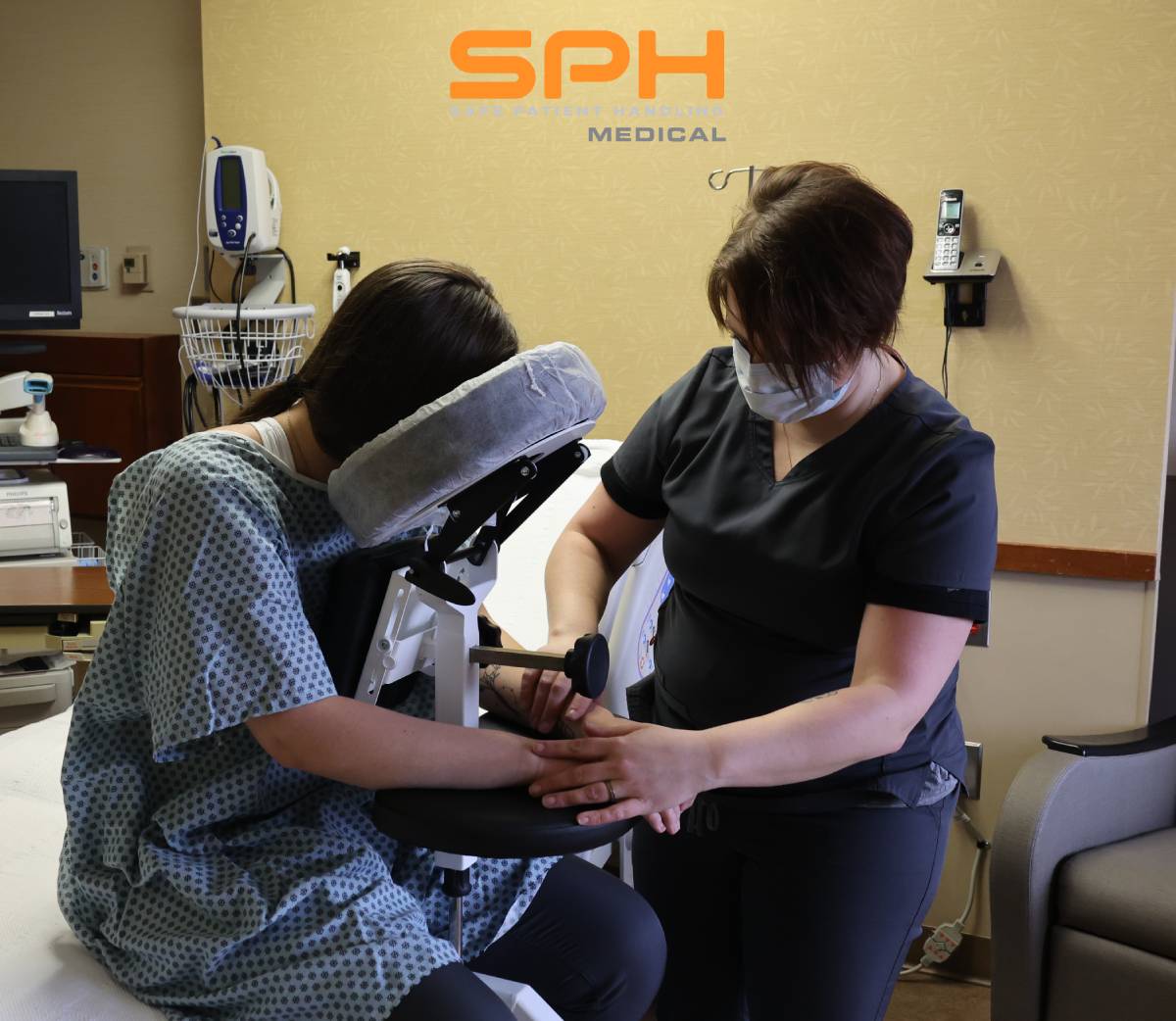
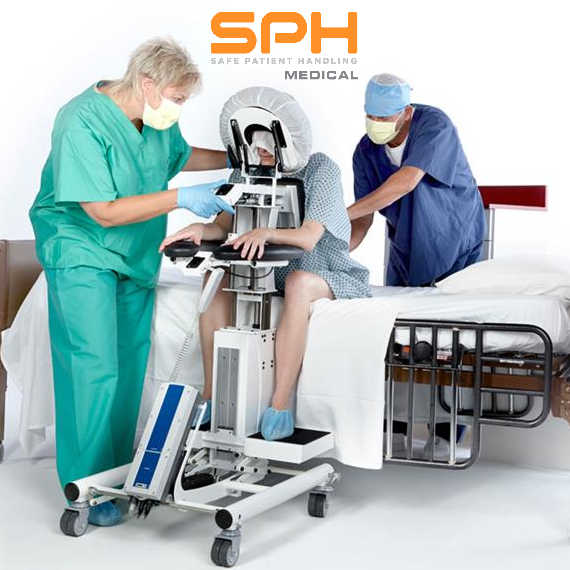
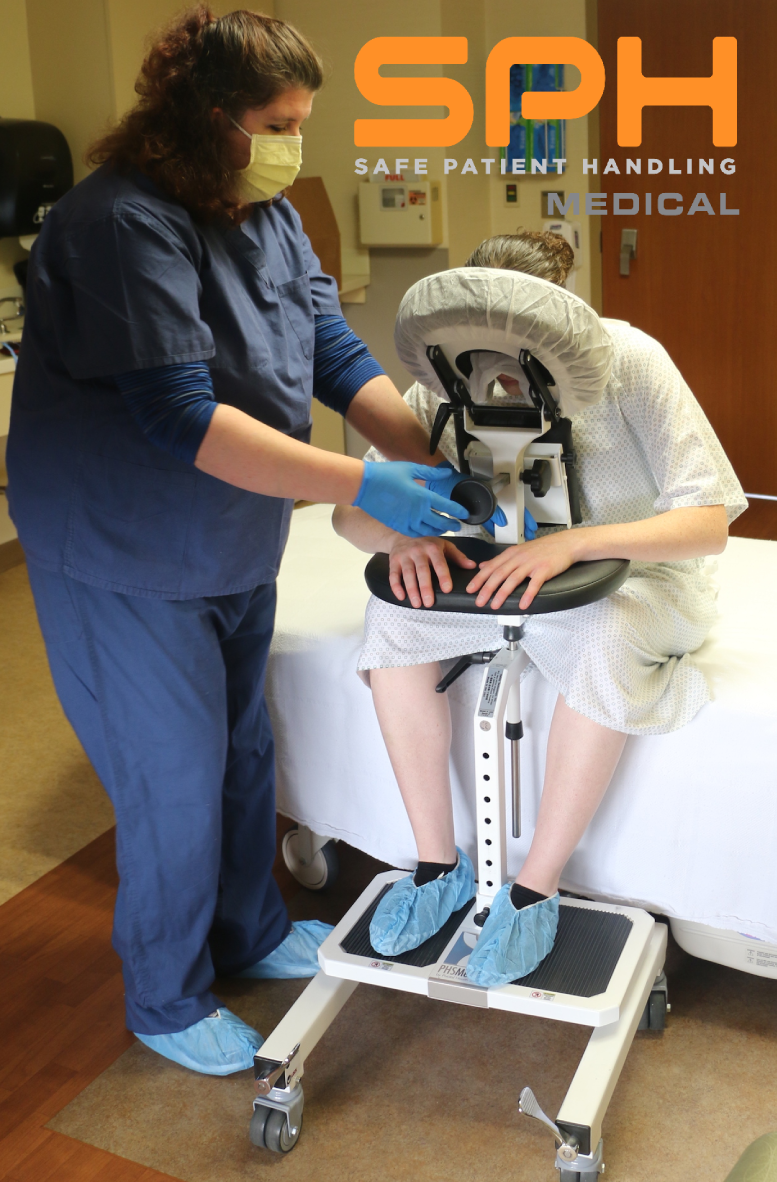
How an Epidural Chair Can Help Improve Hospital Safety
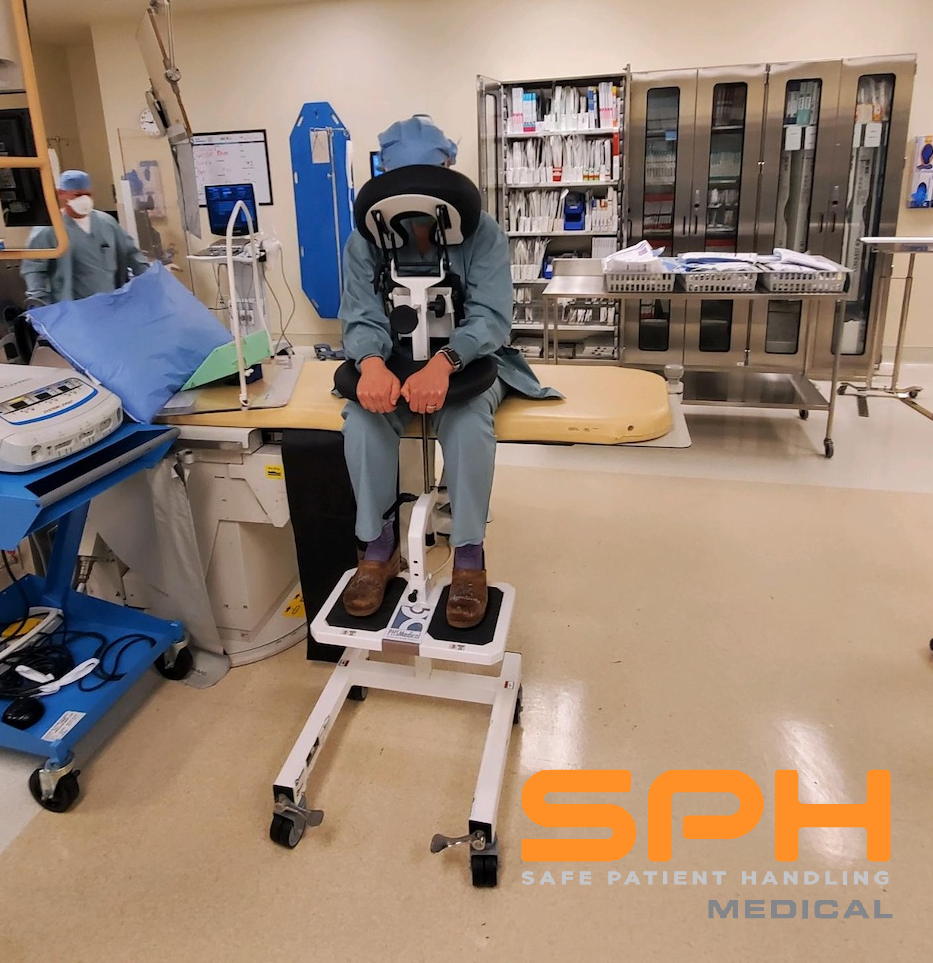
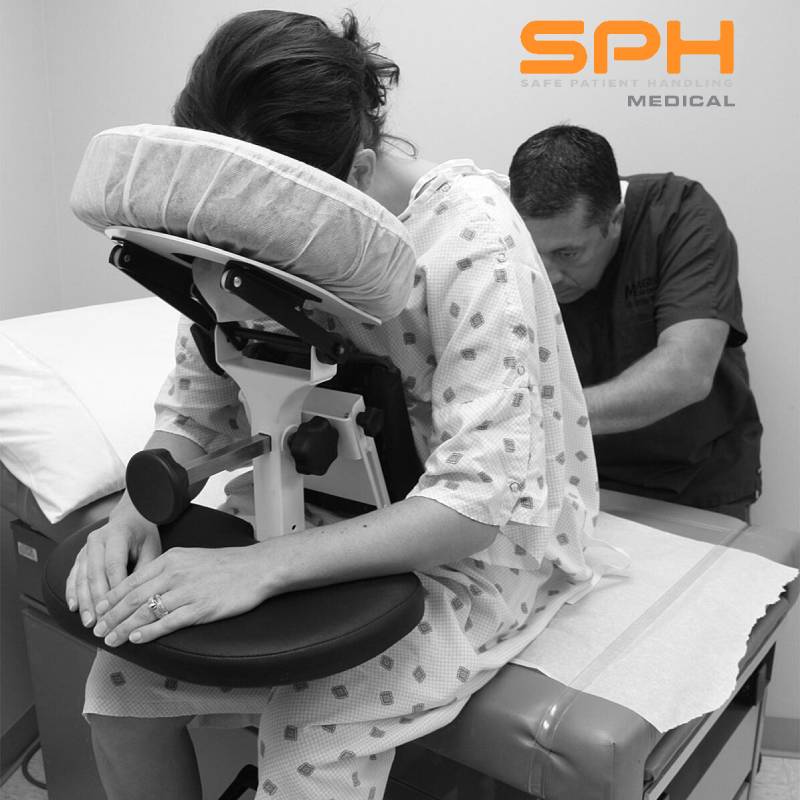
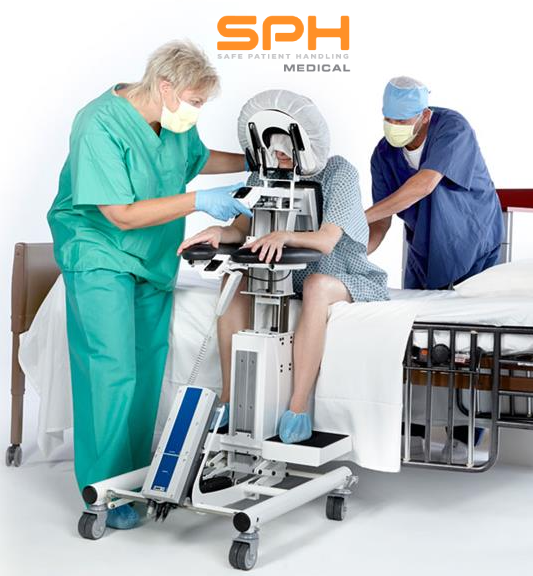
Manually positioning or moving patients from one location to another is the leading cause of injuries among nurses, operating room technicians, and anesthesiologists involved in treating the roughly 324,000 patients who receive spinal blocks each year. These injuries have motivated many hospitals to invest heavily in medical assistive devices to improve patient handling and lower the rate of injuries among hospital workers. One such device is the epidural chair. Also known as an epidural positioning device or an EPD, epidural chairs support the arms, head, chest, and feet of patients receiving spinal blocks. The support they provide minimizes the risk of falls and makes it much easier to transport patients from one location to another as needed for their medical treatments. Studies show that hospitals that use epidural chairs file fewer day-away-from-work cases than those that do not.
Conclusion
Whether we are discussing safety in a hospital’s surgery department or its labor and delivery unit, EPDs should be part of that discussion. And this is because they make epidural pain relief via spinal blocks easier and markedly safer for everyone involved.