Healthcare settings have a paramount duty to ensure both patient and staff safety including safe patient handling in surgery departments. However, one critical aspect often overlooked is the risk associated with manual patient handling in surgery departments. This issue has become a significant concern due to its dire consequences on caregiver health and hospital operations.
The Risks of Manual Patient Handling
Manual patient handling poses considerable risks to healthcare providers. According to a study published in the Journal of Advanced Nursing, nurses involved in manual patient handling activities experience a high rate of musculoskeletal injuries1. Another study found that there was a notable increase in musculoskeletal injuries among hospital patient care staff before the implementation of patient lift and transfer equipment.
Why This Problem Exists
The continued use of manual patient handling can be attributed to several factors, including a lack of awareness about the risks, inadequate training, and the gaps in supply and backorders of safer patient handling equipment. These gaps can lead to situations where caregivers have no choice but to resort to manual patient handling, putting themselves at risk.
In the bustling environment of a surgery department, healthcare professionals are constantly faced with various manual patient handling tasks. These tasks, while essential for patient care, can pose significant risks for injuries to staff members.
Common Manual Handling Tasks in Surgery Departments; Lateral Transfers
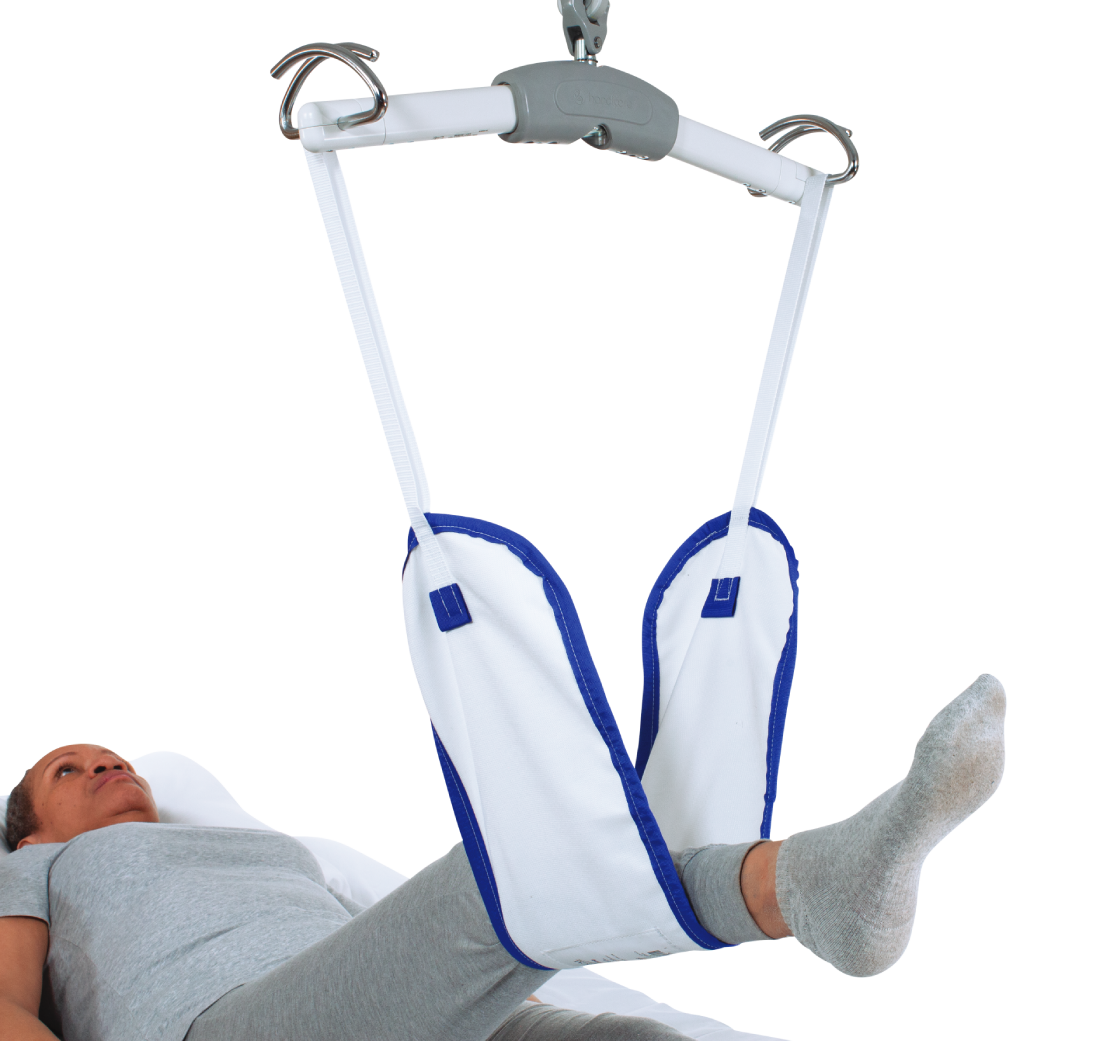
One of the most predictable and frequent tasks is the lateral transfer of patients on and off the operating table. When a patient is sedated for surgery, they become entirely dependent on the healthcare staff for movement. This dependence increases the physical demand on the healthcare professionals, leading to a higher risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
Limb Holding
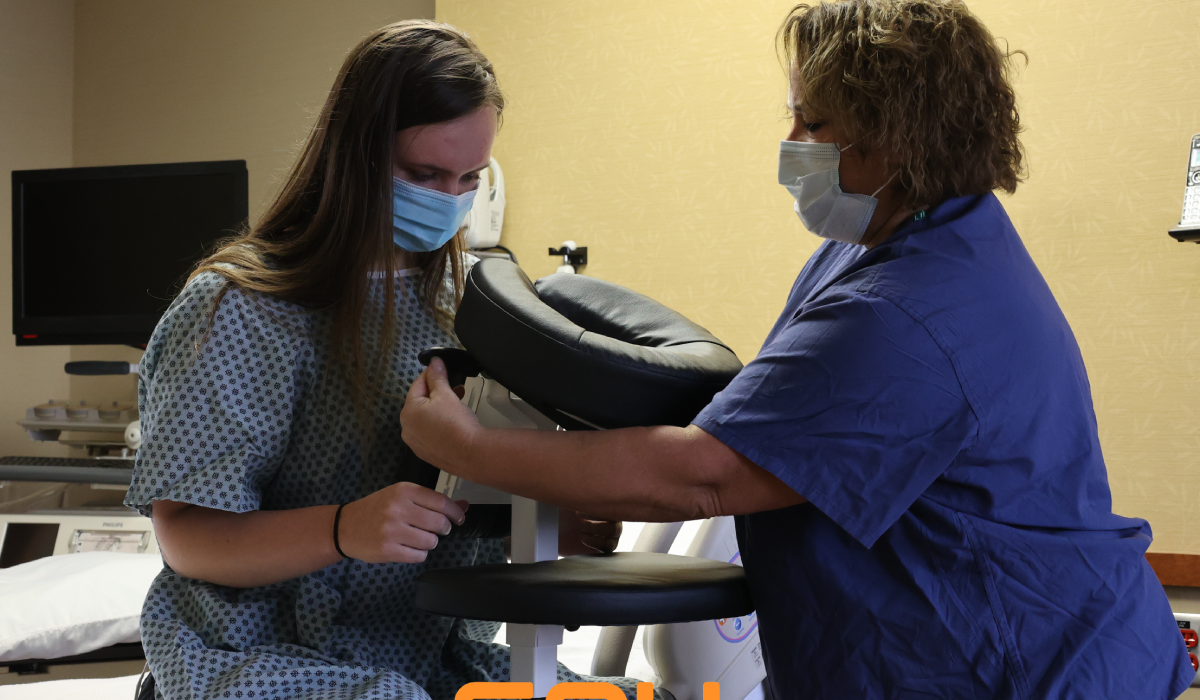
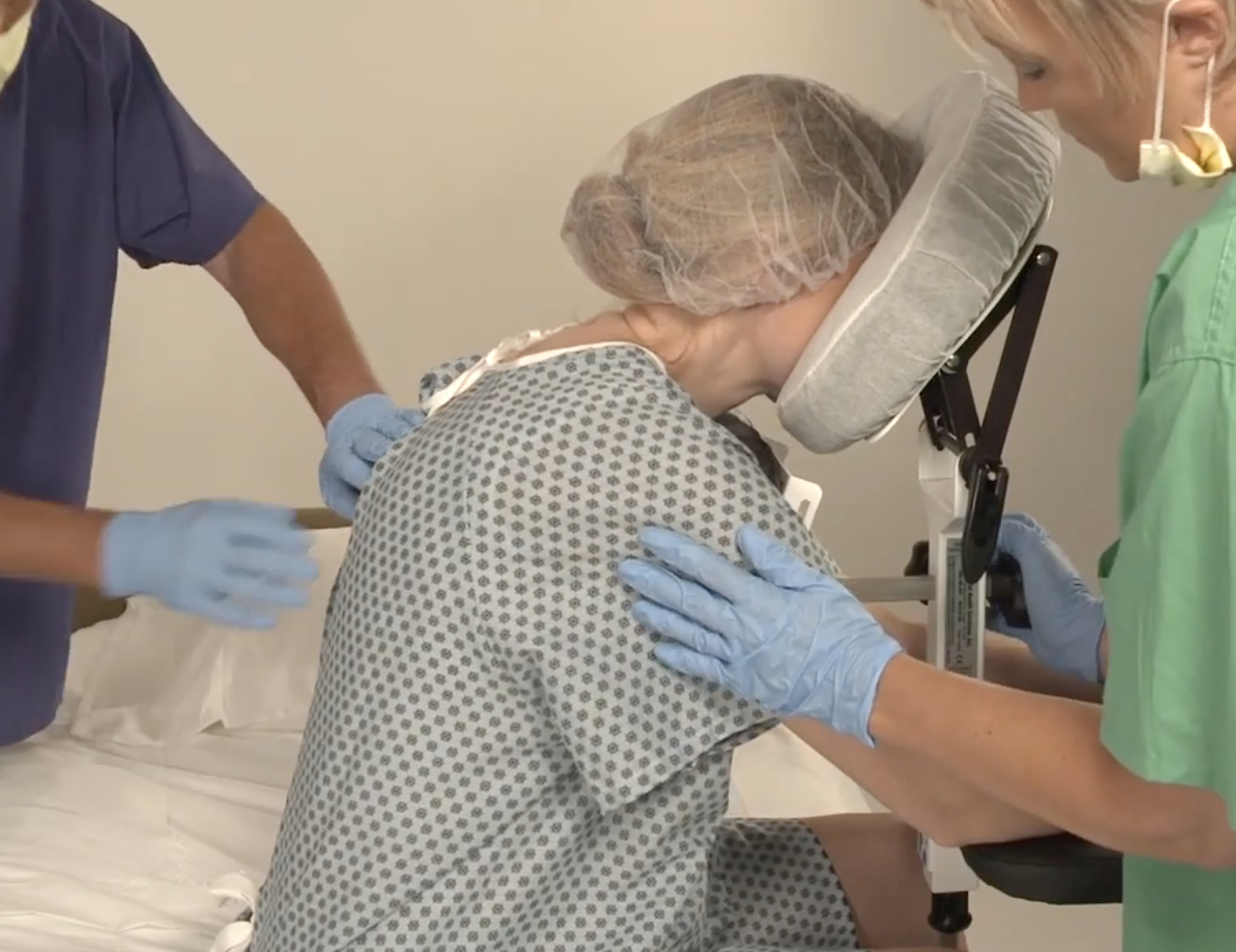
Another common task is limb holding during surgical procedures. This task requires nurses and techs to maintain a steady hold on a patient’s limb for extended periods, often in awkward postures. This static strain can lead to musculoskeletal disorders such as back, neck, and shoulder injuries.
Turning Patients
Turning patients to a prone position is another routine task that can be hazardous. It involves manually rolling the sedated patient onto their stomach, which can be particularly challenging for heavier patients. This activity puts a lot of strain on the caregiver’s body, increasing the risk of injury.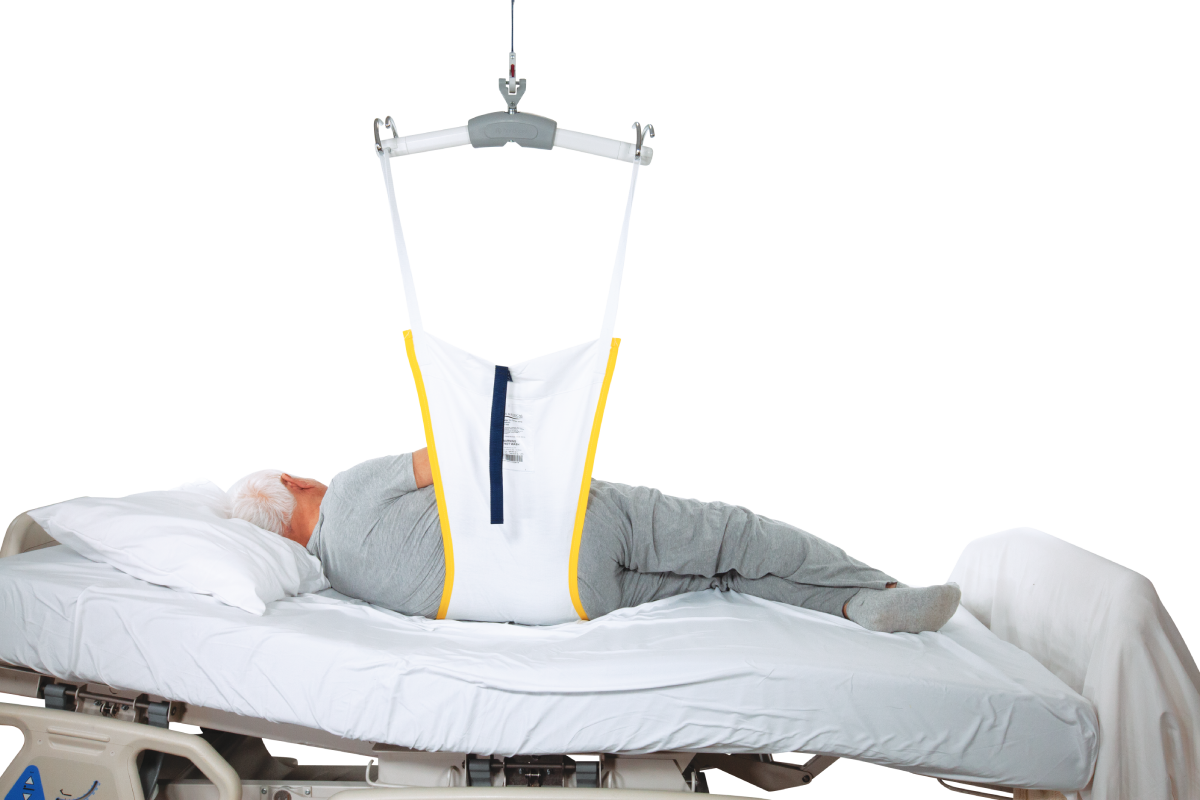
The Need for Safe Patient Handling
Given the inherent risks associated with these tasks, it’s clear that there’s a crucial need for safe patient handling practices in surgery departments. Implementing safe patient handling interventions can significantly reduce overexertion injuries by replacing manual patient handling.
Moreover, the use of safe patient handling technology can mobilize patients gently, earlier, and progressively without risking injury to caregivers. It’s time to transform the way we handle patients in surgery departments – for the sake of both patient and staff safety.
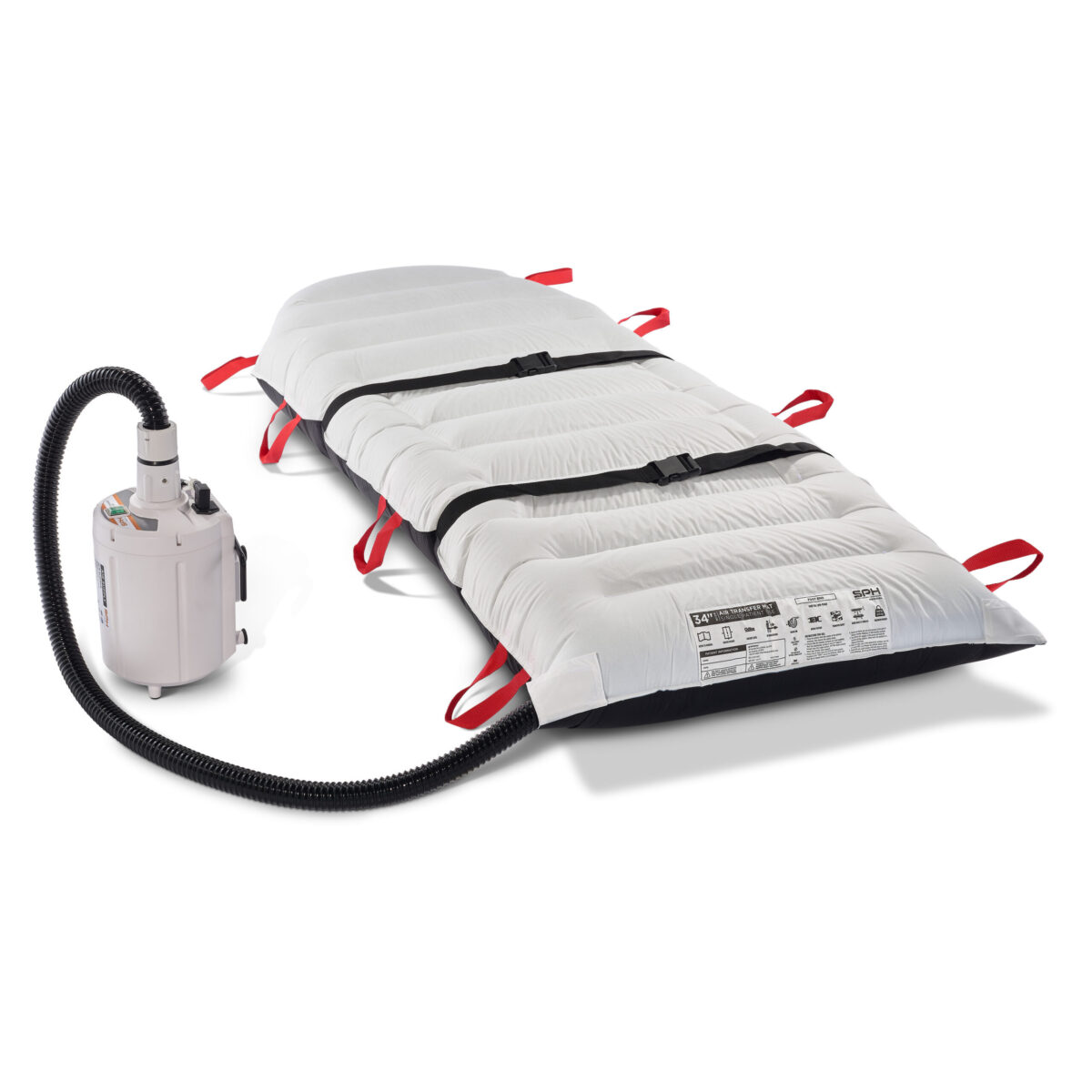
The SPH Medical Air Transfer and Positioning System: A Gold Standard Solution
The SPH Medical Air Transfer and Positioning System is a revolutionary product designed to mitigate the risks associated with manual patient handling. It uses air-assisted technology to facilitate safe and efficient patient transfer and positioning, significantly reducing the physical strain on caregivers.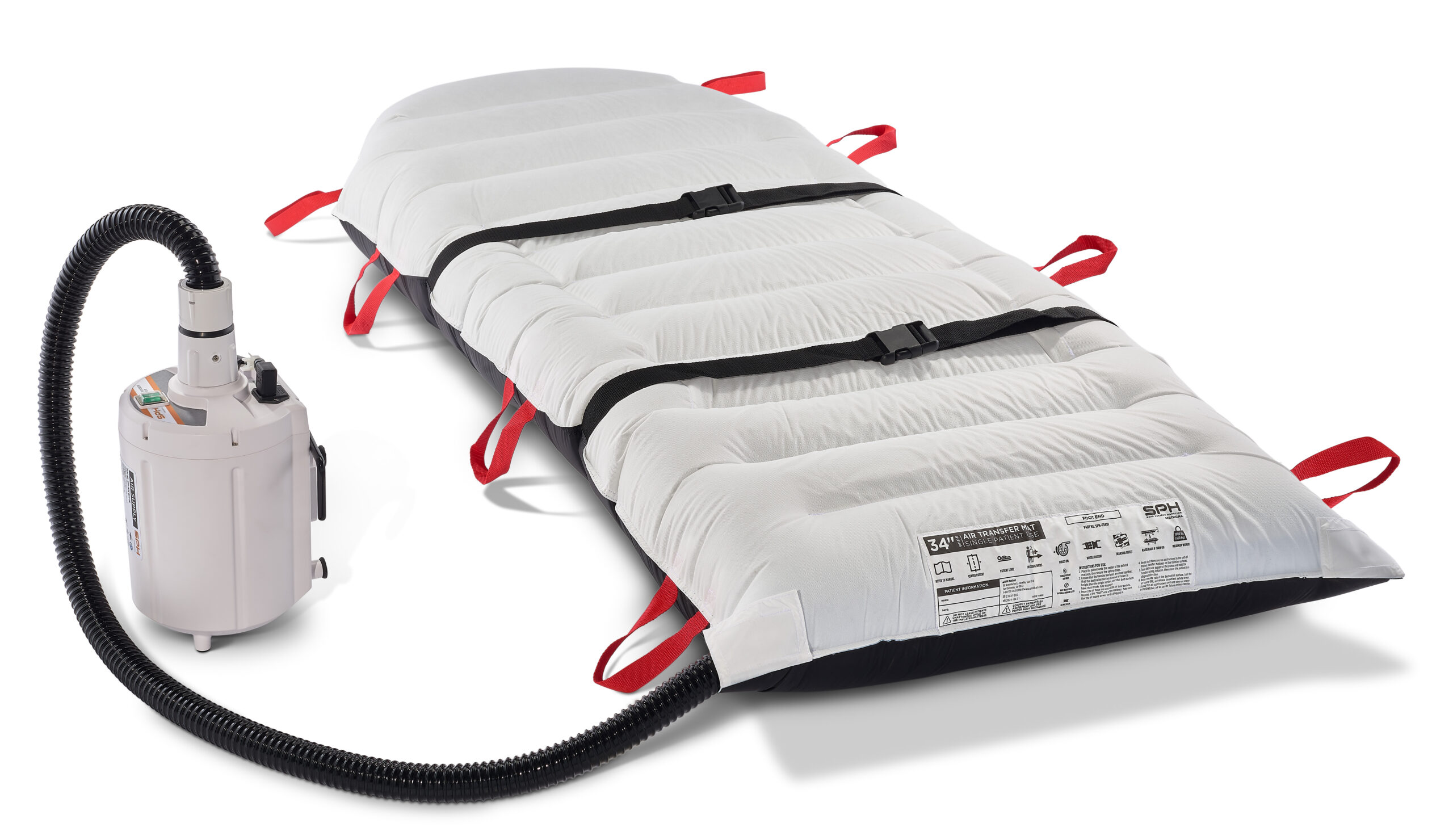
Why It’s the Best Solution for Safe patient Handling in Surgery Departments
When compared to other patient handling methods, the SPH Medical Air Transfer and Positioning System comes out on top. It has been proven to reduce the risk of injury while performing patient handling tasks, specifically those predictable lateral transfers on and off the OR table. The 1000 lb weight capacity and variety of transfer mat sizes allow this solution to be used for all surgery patients. Moreover, it is considered a “gold standard” and a “trusted partner” for hospitals looking to improve patient and staff safety.
Cost-Effectiveness of the System
The costs associated with manual patient handling are staggering. These include direct costs such as treatment and rehabilitation for injured staff, and indirect costs like lost productivity and potential lawsuits. Investing in the SPH Medical Air Transfer and Positioning System can significantly reduce these costs. The system’s efficiency and reliability translate into fewer injuries, less downtime, and a safer working environment, making it a cost-effective solution for hospitals.
Conclusion: The Clear Choice for Enhanced Safety and Efficiency
The risks associated with manual patient handling in surgery departments are clear and present. However, solutions like the SPH Medical Air Transfer and Positioning System offer a way forward. This system not only improves patient and staff safety but also proves to be a cost-effective solution for hospitals.
By addressing critical supply needs and implementing safe patient handling systems, hospitals can significantly reduce workplace injuries, improve staff morale, and ultimately enhance patient care. Contact SPH Medical today to explore how this system can revolutionize your patient handling procedures.