A Sustainable Process for Early Patient Mobility with RoWalker
When patients are critically ill, they may require a ventilator to support their breathing as they recover. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, ventilator assisted breathing is a standard treatment during the worst phases of the illness. While this treatment is necessary and life-saving, prolonged ventilation can have negative effects on patient outcomes. When medical procedures require sedation, the patient must rest in bed for days at a time. The human body is made to move, so extended periods of being bedridden will weaken the core muscles that sustain patient mobility. This is often referred to as deconditioning. Sedation and bedrest also disrupt the circadian rhythm of waking and sleeping. Patients may suffer from sleep deprivation and delirium after a time. These physical and mental side effects have the practical result of lengthening a patient’s hospital and rehabilitation stay. At hospitals under stress, patient beds are at a premium. When one patient is recovering at the facility, it prevents a new patient from receiving care. Also, a lengthy stay leads to higher medical bills and financial stress for patients and families. This is why team members need to collaborate to develop a nurse driven early mobility protocol.
Developing a Process for Early Patient Mobility
To improve patient outcomes a multi disciplinary approach including Nursing Leadership, Physical Therapy, and respiratory team members need to collaborate to develop a nursing driven early patient mobility protocol. No one wants to rush patients through the recovery process. However, if a patient can come off the ventilator and start moving, it will lead to an improved outcome. Determining if a patient is ready for early mobility takes several steps.
Reduced Sedation
It is difficult to evaluate patients who are deeply sedated. To measure progress, the staff should work to minimize the sedative dose so that it is easier to interrupt sedation. When the patient can handle the reduction safely, staff members can take the next step in evaluation.
Spontaneous Waking and Breathing
During an interruption in sedation, the medical staff can determine if the patient can breathe without assistance. They can also begin to assess the mental state of the patient.
Early Mobility Intervention
When a patient is mentally and physically stable, mobility therapy can begin while in the ICU. This treatment may only involve a few steps, but it is important progress for the patient.
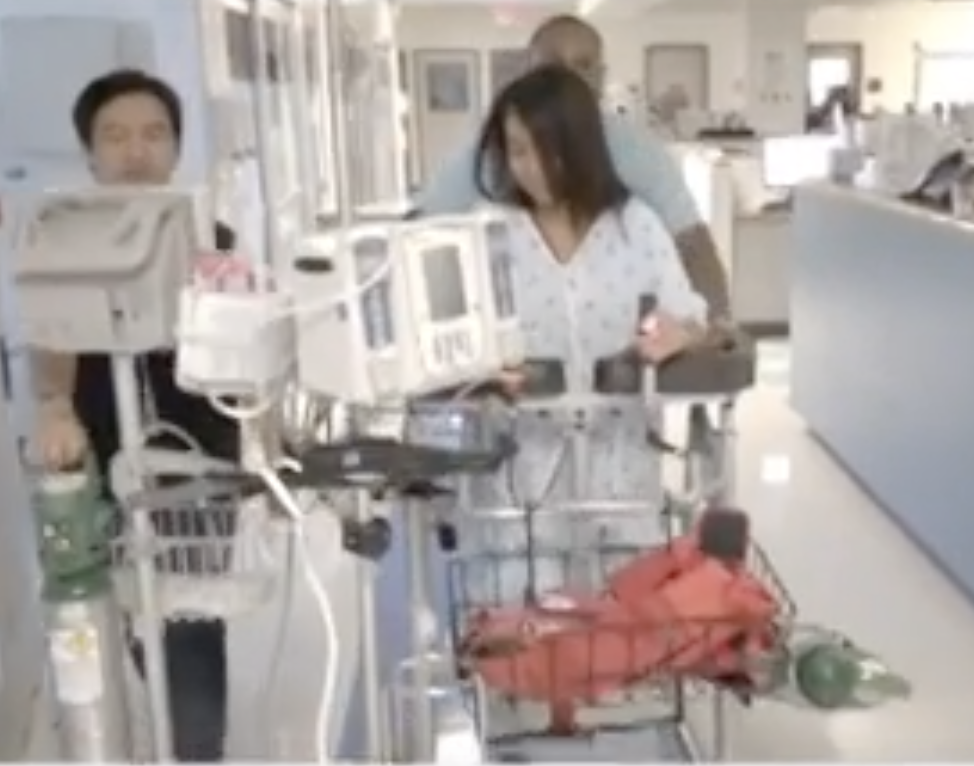
RoWalker: Focusing on Patient and Staff Safety
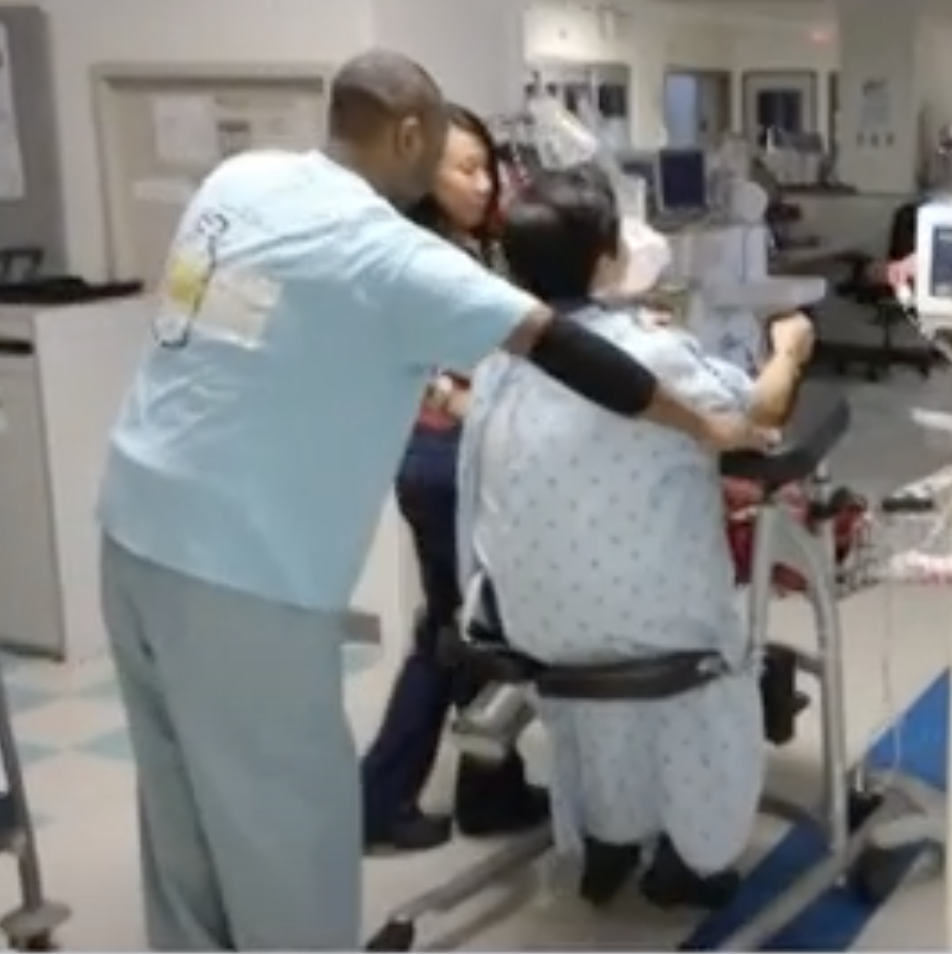
Improving patient mobility involves a fall risk for patients, and it can create a personal safety risk for nursing staff. Without the right equipment, the patient will depend on a staff member for support. A sudden stumble can lead to strained muscles and other injuries for staff members. A serious fall will be a setback for the critical patient.
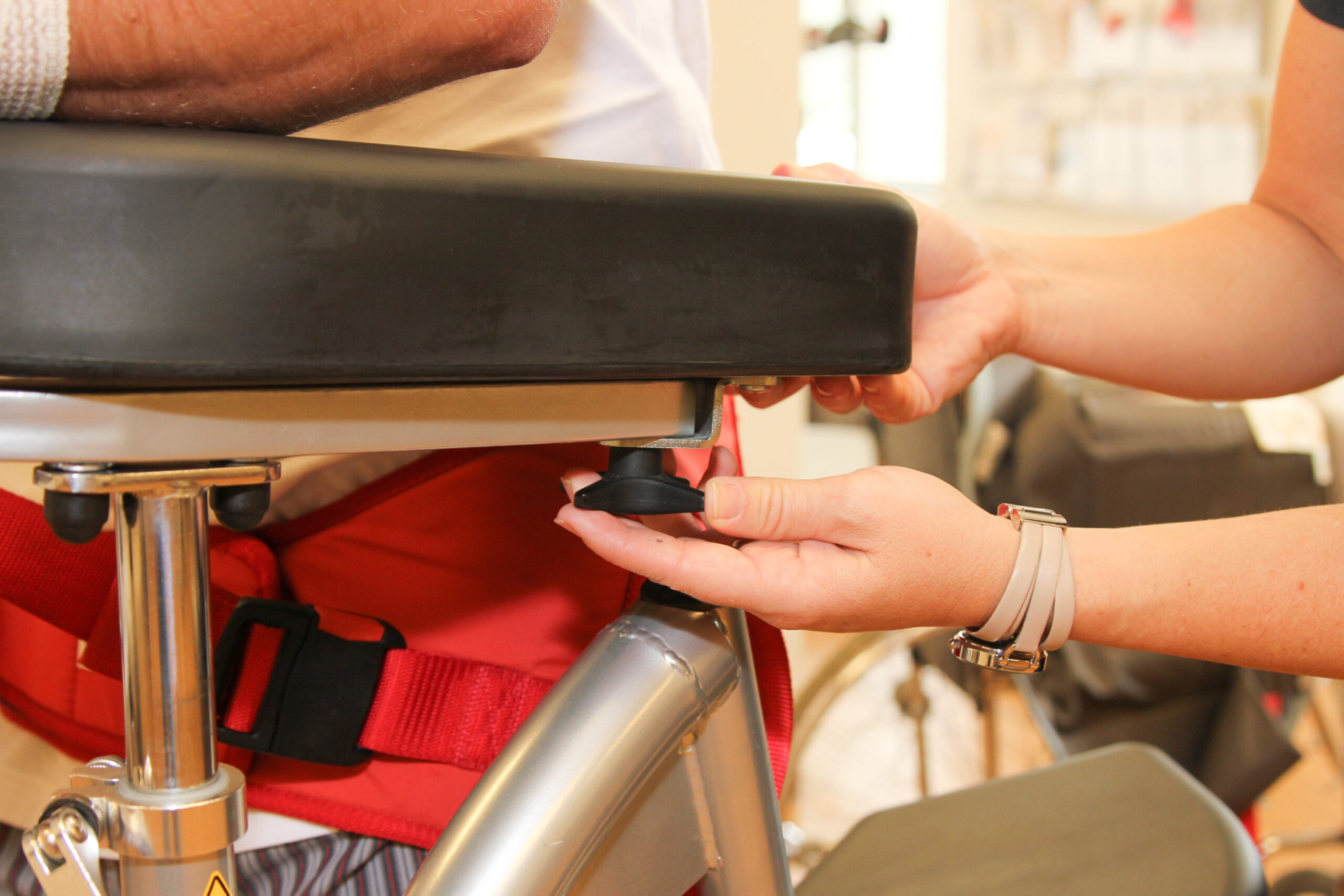
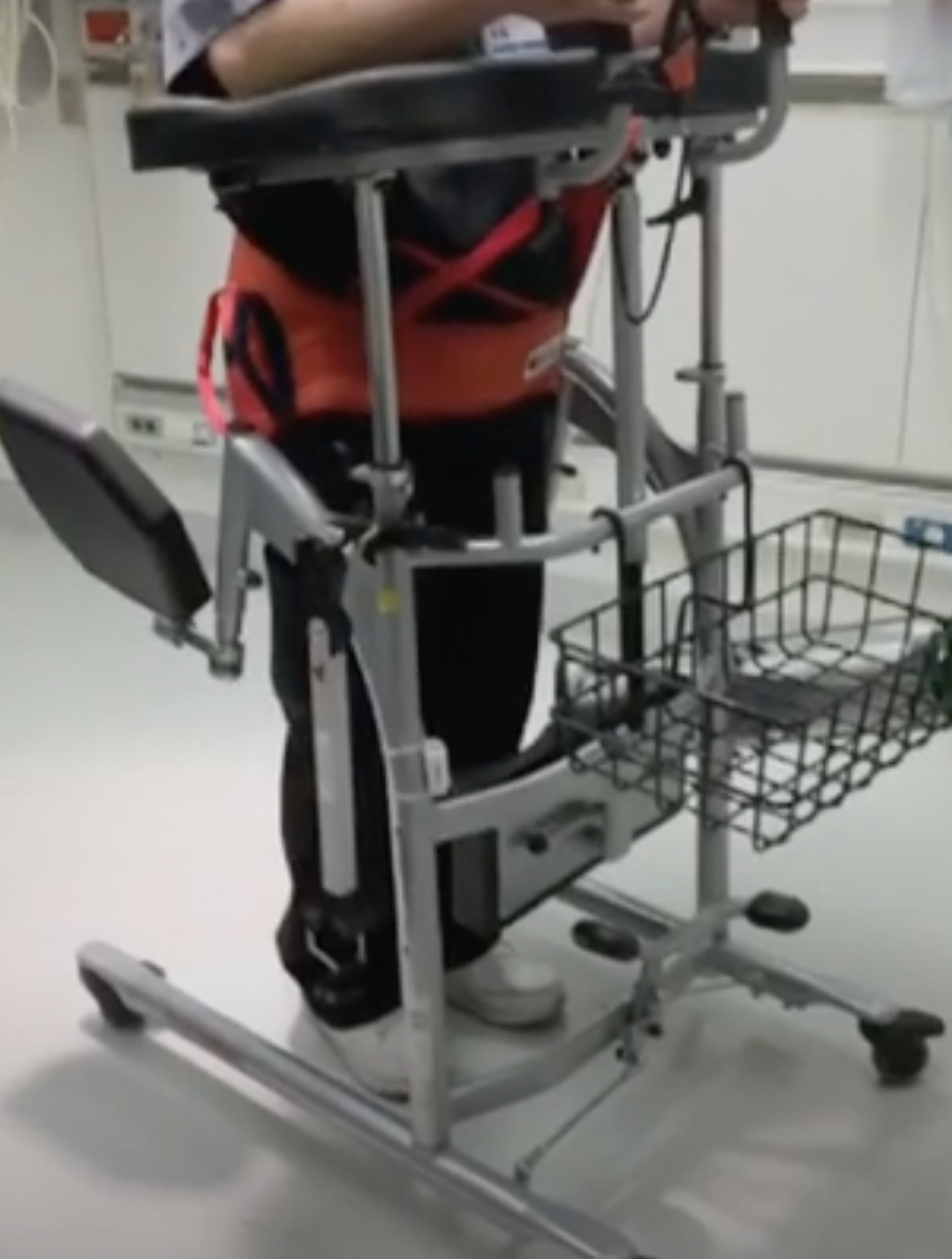
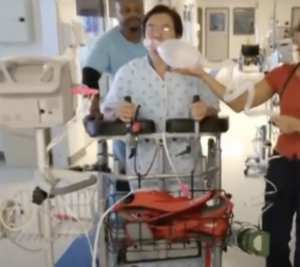
The SPH Medical RoWalker provides a sturdy framework with fall prevention in mind. The adjustable settings allow staff members to prepare the device for each patient. A cushioned platform gives the patient a place to support his or her upper body.
Lower body support belts and seating pads prevent patients from falling when tired.
The RoWalker can accommodate the needs of ICU patients. It has integrated features such as a telescoping IV pole, oxygen tank holder and a front-facing basket for cardiac monitors.
Seeking the Best Critical Patient Outcomes
A nurse driven early mobility supportive device like the SPH Medical RoWalker does more than provide an early physical therapy and nursing intervention. It offers a positive experience for the patient. When patients see that they can take a few assisted steps, it gives them a sense of hope for the future. Working with mobility also provides nursing staff with a metric for patient improvement as they extend the distance walked during each session.
The SPH Medical RoWalker combines fall prevention with early mobility intervention. Employing this device with a mobility protocol will decrease the length of hospital stays and increase positive patient outcomes.