The Epidural Positioning Device Improving Spinal Block Safety
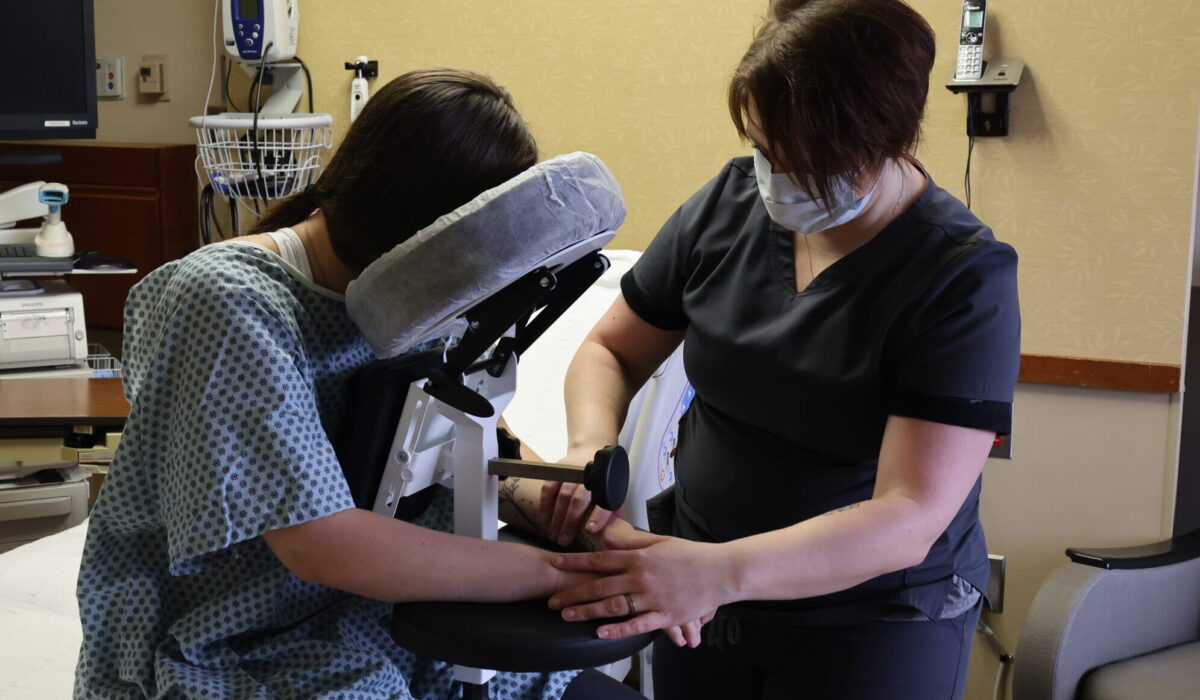
There have been many advancements in Safe Patient Handling over the recent years. One very simple advancement has been the SPH Medical Epidural Positioning Device. This simple tool offers improved patient comfort and safety while positioning patients in the ideal flexed spine position. Most importantly it protects the caregivers, nurses, and anesthesia techs that use it and prevents staff injuries. When patients have surgery like a hip or knee replacement or go into labor before delivering a baby, they are commonly given pain relief via an epidural injection or spinal block. Any hospital unit can utilize an epidural positioning device (EPD) to improve a patient’s stability and comfort while they are receiving a spinal block. This device, also known as an Epidural Chair, decreases the risk of musculoskeletal injury to clinical staff as they position a patient to provide an epidural procedure as well as improves spinal block safety. Using this specialized equipment makes it easier for nurses, anesthesiologists, and other health care professionals to engage in safe patient handling practices at all times.
Many surgeons who perform complete knee or hip replacements prefer to recommend spinal blocks rather than general anesthesia for their patients. This treatment allows patients to start moving right away as they recover from surgery. The epidural positioning device can safely position patients in a seated position during many different types of procedures. Nursing staff and other qualified medical professionals in a Surgery Department or Labor and Delivery Unit can make adjustments to the device so that it can accommodate a variety of body types.
Safely Perform an Epidural or Spinal Blocks with the EPD
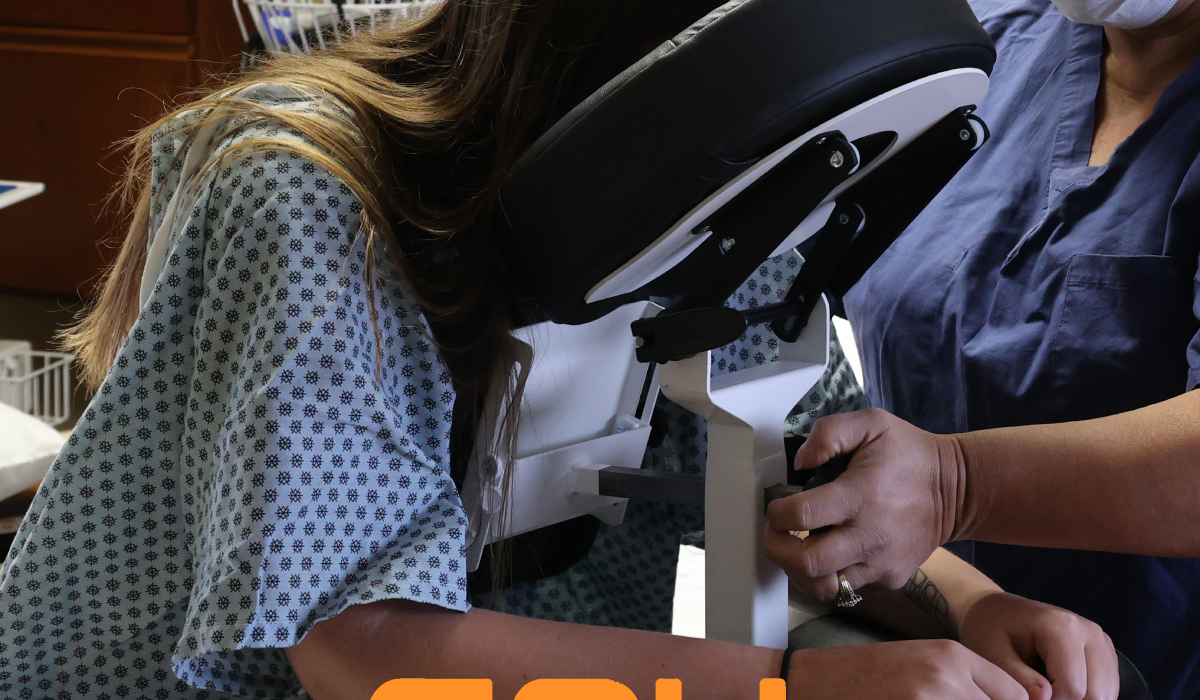
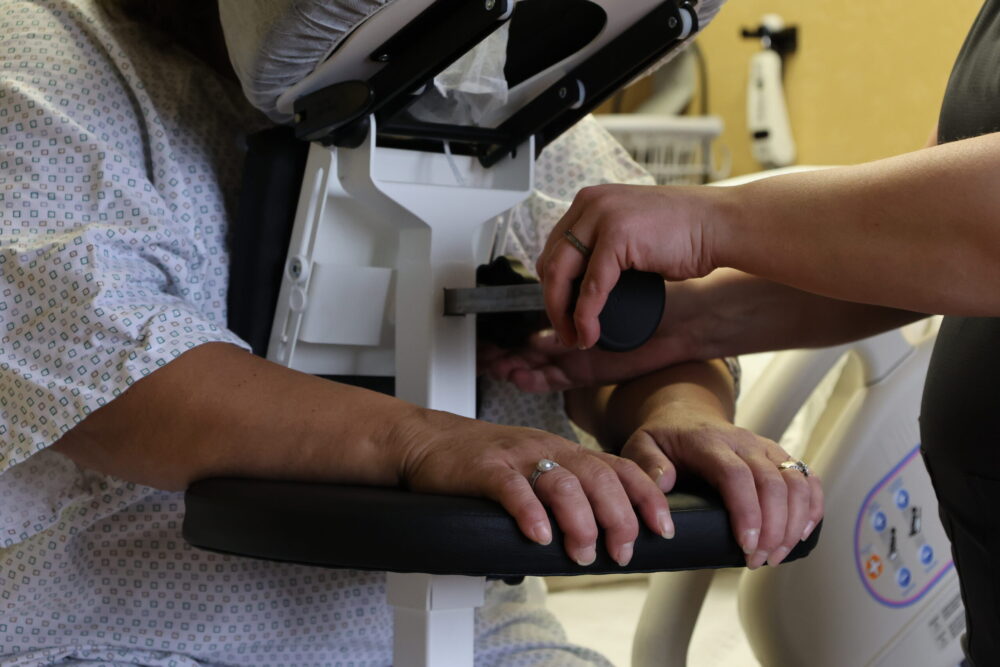
When a patient is seated at bedside or on a stretcher supported by an Epidural Chair, medical professionals can safely perform a spinal block or epidural procedure without difficulty. Funny enough, it’s not actually a chair as it has no seat! The patient actually sits on the bed or gurney and The EPD is brought over to them to provide support. As a patient leans forward against the EPD, the device promotes an ideal degree of thoracic, lumbar, and cervical spinal flexion that makes it easy for an anesthesiologist to insert a needle between their vertebrae. The specialty chair supports the patient so that staff members will never need to use their own weight to stabilize, hold, fix, or balance their body. Nurses and other clinical professionals who bear the weight of their patients can suffer sustained physical stress that can damage their own joints after a period of time. An unstable, large, or medicated patient can easily harm a staff member via improper physical contact. Using this specialized chair also decreases the chance that a patient or staff member will be injured from a slip or fall. Injuries can also be caused when sliding or rolling furniture or equipment strikes or collides with a patient or staff member.
An Epidural Chair can greatly benefit a hospital’s orthopedic surgery department or labor and delivery unit. This device is easy to add to any inventory of essential equipment. Keeping and using an epidural positioning device may increase spinal block safety and decrease a hospital’s risk of liability. According to researchers at Stanford University, the number of annual epidural procedures undertaken in the United States is increasing. The journal Anesthesiology published a report in 2018 stating that from 2009 to 2015, a large percentage of the 17 million women who delivered babies received a spinal analgesic. 68% of women who were at a normal weight and 76% of women who were overweight received this epidural treatment during labor. In 2008, 10% fewer pregnant women received the same epidural procedure. As spinal blocks become more frequent, patients and staff face greater chances of experiencing accidental injury, doing harm to equipment, wasting time, and enduring unfortunate or unsatisfying situations. Adding an EPD to a hospital’s depository of specialty equipment promotes safety and well-being for staff and patients and enhances the overall healthcare experience.