Epidural Pain Relief: Positioning for maximum safety
An epidural, is often used throughout the U.S. to relieve pain during contractions and delivery without restricting the mothers’ ability to have control and strength to push the baby out. For an epidural, medicine is administered through a tube inserted by the anesthesiologist in the lower back. A mixture of anesthetics and analgesics can be included in the epidural for women who are delivering vaginally. The medicine will cause a loss of sensation in the lower extremities and the mother is still awake and alert. The epidural provides the needed pain relief for the mother to bear down to push the infant through the birth canal successfully. For women who are having a cesarean delivery, the anesthetic dose in the epidural can be increased. This type of epidural causes a loss of feeling in the lower half of the woman’s body. Epidural pain relief may also be necessary for some patients after delivery.
Why Is Proper Positioning Important For an Epidural?
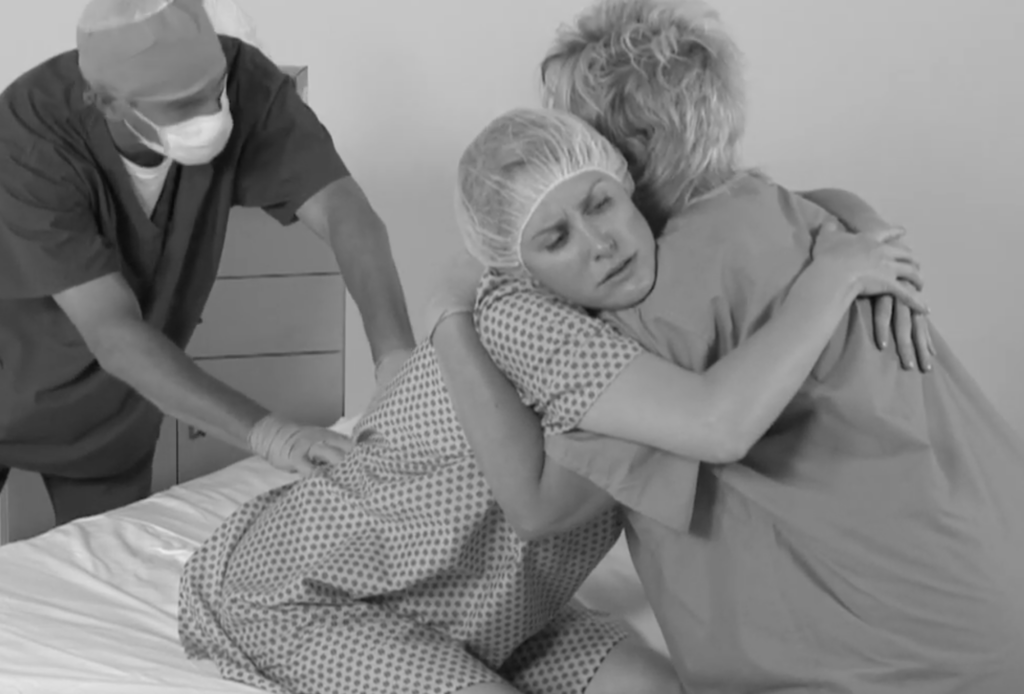
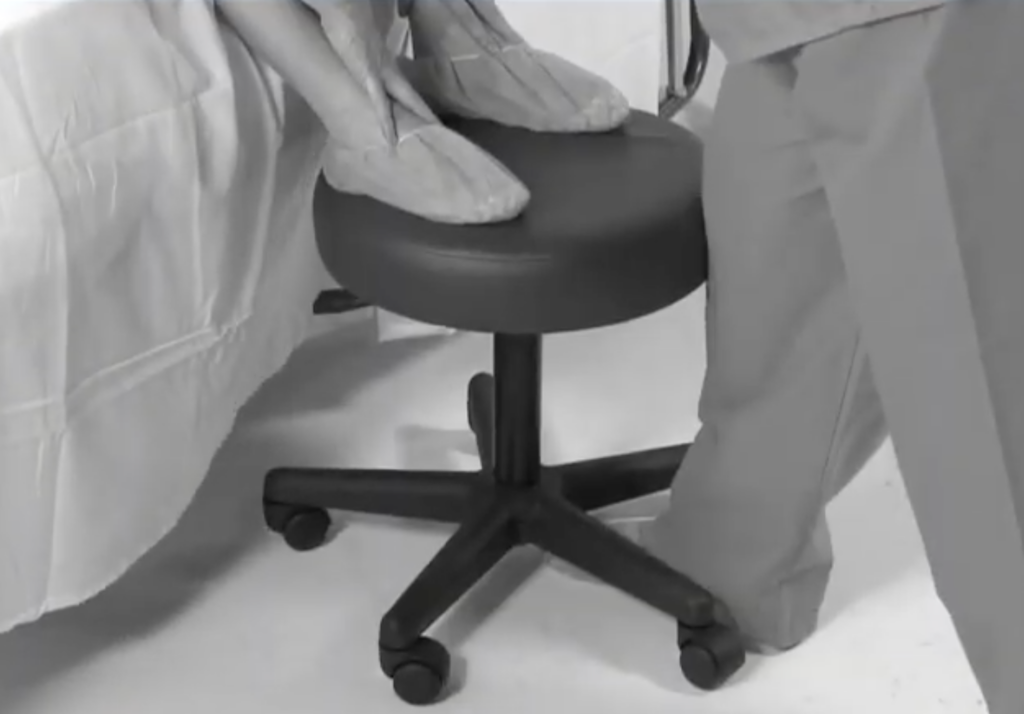
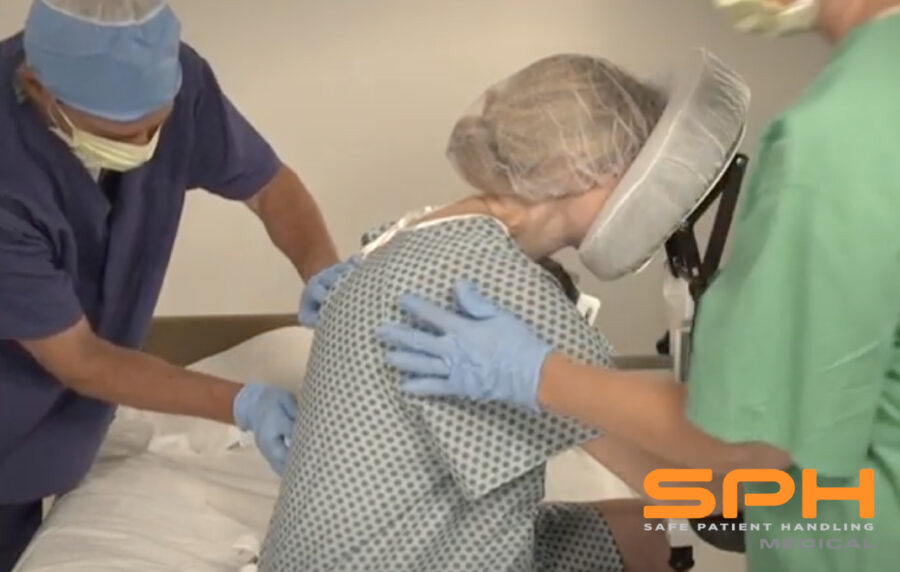
The patient’s position is very important for the epidural to be administered properly, reduce the risk of side effects, and adequately reduce pain during labor. Nursing safety is also an important concern during patient positioning and epidural placement. There are two typical positions for the patient to be positioned in for optimal placement. First, there is the side lying position. In this position the patient should lay on their side in bed to allow the Doctor to access the spine. The second position is a sitting position at the edge of the bed leaning over a pillow with knees raised to create sacral curvature. The legs are typically raised by having the patient put her feet on a stool. Medical staff will assist the patient to ensure she is in the correct position before and during the epidural block.
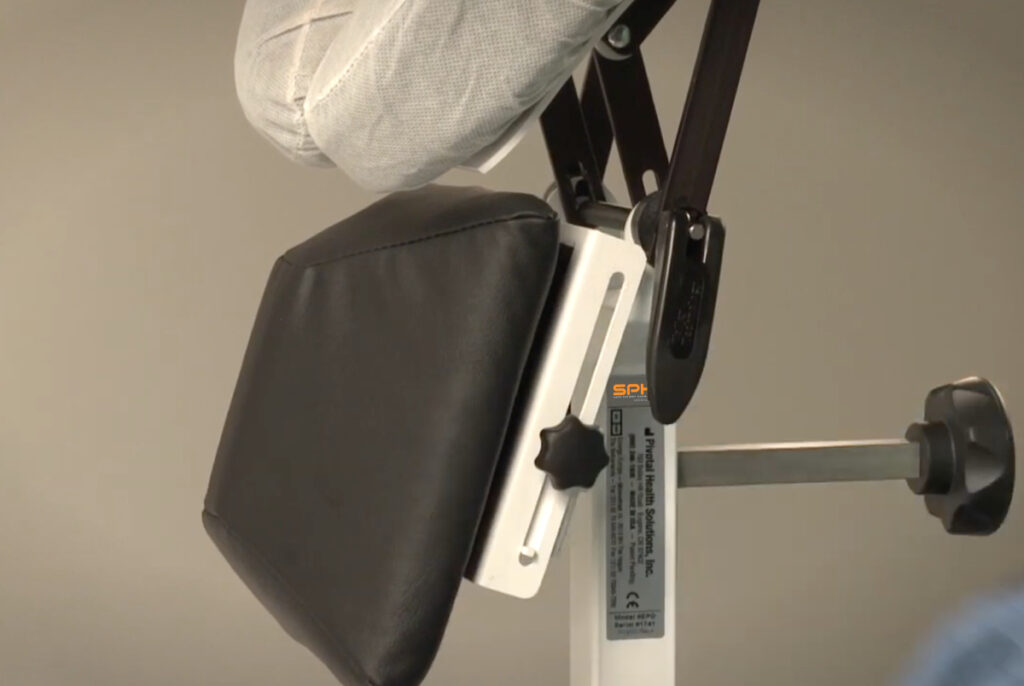
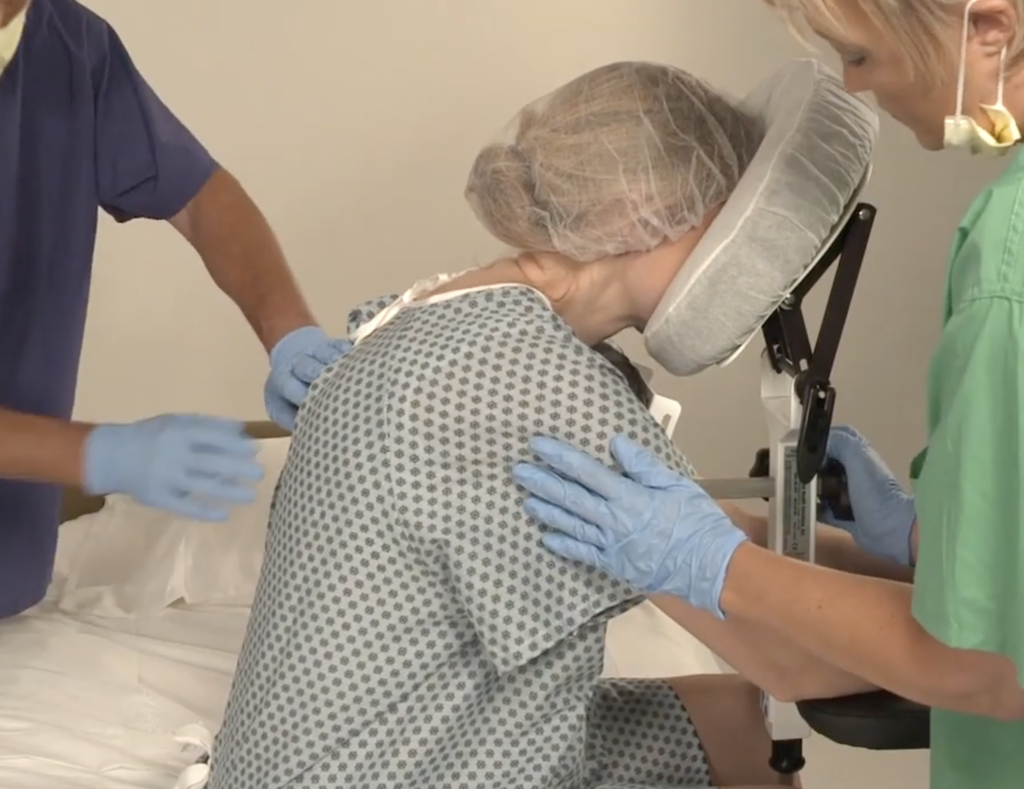
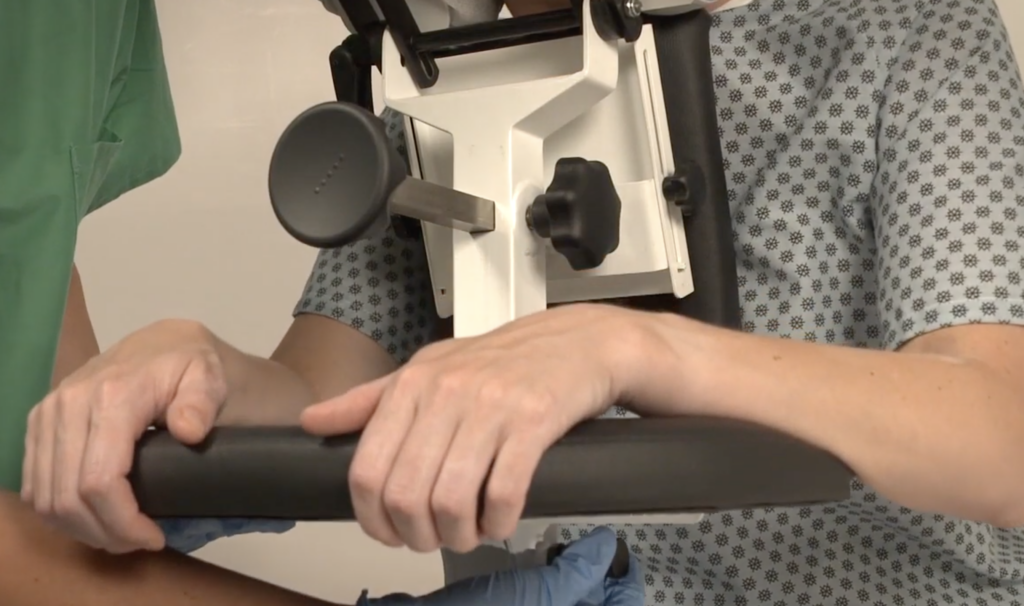
For maximum safety and secure positioning, the nurses can bring in an epidural chair. The epidural chair, also known as an EPD, or epidural positioning device makes it more comfortable for the patient and safer for everyone. The EPD ensures that the patients’ back is curved and they are fully supported without having to lean on a nurse! The EPD has a head rest, arm supports, a central pad that extend toward the patients chest to promote spinal flexion, and a foot plate for support. All these components are adjustable to fit the needs of each patient. Proper positioning of the body reduces the risk of error or complications when the epidural is placed.
Avoiding manual patient handling is important for nurses to remain safe during the Epidural procedure. The EPD Solves this problem. In the image below the nurse is supporting the patient and putting her neck back and shoulders at risk.
Stools that don’t lock can create unnecessary risks for patients and nurses.
The epidural is performed under local anesthesia using a sterile technique. When the nerves of the skin are numb from the local anesthetic, the epidural needle is inserted between the spine area of the lumbar vertebra to get to the “epidural space,” which is just outside of the spine. This space contains the spinal nerves and cerebrospinal fluid. When anesthetics are administered to this area, the pain of childbirth is reduced. Most of the time, epidural pain relief is continuous, which means the medical staff will place a soft, small catheter or tube into the epidural space with a needle. A sterile dressing is used to secure the tube to the patient’s back. This constant flow of medication is continuously administered to the patient during labor and delivery to reduce pain and discomfort.
What Are the Risks to the Patient?
Epidurals are generally safe, especially if the patient was sitting in an epidural chair to receive the medication. However, in some cases, patients can experience:
- Nerve pain
- Significant drop in blood pressure, which can cause nausea and lightheadedness
- Itchy skin
- temporary loss of bladder control
- General sick feeling
- Headaches
Once the epidural anesthesia begins to wear off, it is common for patients to feel numbness in their legs until the medicine has completely worn off, which can take a few hours. It is best for the patient to sit or lie down until feeling in the legs is restored. Patients will often feel tingling in their legs after the epidural is removed, but this symptom is temporary. Patients are advised not to operate machinery, consume alcohol, or drive for 24 hours after the epidural is removed.
How Does an EPD Reduce the Risk or Injury to Nurses Administering the Epidural?
An epidural positioning device not only makes medication administration more comfortable for the patient but also keeps nurses from sustaining work-related injuries, MSD’s. When a nurse has to statically hold the patient in position, support the patient or catch a falling patient, this could cause injury to the nurse. Using the EPD means that the patient is properly supported and in the ideal position every time. The EPD becomes a standard of care. Using the EPD that will position the patient comfortably so the nurse can provide effective care as efficiently as possible with the best possible outcome.
Epidurals are a safe choice for many women who want to manage the pain of labor and delivery. The procedure is recommended by Anesthesiologists for optimal pain relief.