What is Epidural Safety?
Epidural Analgesia’s are used to reduce or completely eliminate pain. It is when the doctor inserts opioids or local anesthesia in their patient’s epidural space, which blocks the nerve roots. Staff and patients can be protected from injury when exercising epidural safety during this procedure.
Local anesthesia can include opioids such as morphine, hydromorphone, and fentanyl or drugs of a different class such as mepivacaine, lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine. Mepivacaine and lidocaine can last up to 2.5 hours. Bupivacaine and ropivacaine are the options of choice for continuous epidural effusion because they last 4 to 7 hours. The walking epidural is a mix of narcotics, epinephrine, and local anesthesia that the doctor inserts into the patient’s epidural space.
Epidural Analgesia’s are often used during child birth to assist the woman in managing her pain. They are also utilized during surgery to numb the patient. Epidurals are often effective in blocking pain from the waist down. Their dosage is calculated by an anesthesiologist based on the type of epidural and how much of the patient needs to be numbed. They can eliminate pain for people in short term or long term situations.
Common Applications
Epidurals come in different types, depending on what they are being used for. Childbirth uses the standard epidural and the combined spinal epidural, which is also called the walking epidural. The walking epidural involves the administration needle coming in contact with the fluid around the spinal cord, whereas the needle does not meet the fluid around the spinal cord in the standard epidural.
The Benefits for Patients and Nurses
The benefits of having an epidural are plentiful. The walking epidural is beneficial because it allows for the mother to still have an awareness of the lower half of her body when giving birth. This allows the patient and nurse to coordinate the rhythm of her pushes. A walking epidural may or may not allow the mother to do cat and cow stretches. The standard epidural is beneficial because it completely eliminates feeling, which can avoid patients going into shock during invasive surgery, trauma, or child birth.
Epidural Safety and the Risks of Epidurals
The risks for patients when getting either type of epidural are low blood pressure, being mandated to stay in bed, and having to rely on a catheter. The catheter can cause problems such as the rare case of hematoma, epidural abscess, postdural puncture syndrome, and infection at the site of insertion.
Standard epidurals leave the patient with no feeling in the lower extremities, which can prevent the ability to shift in bed and the ability to move the baby into a more favorable position when birthing. Standard epidurals also involve the risk of local anesthetic toxicity, which can present with irritability, seizures, circumoral paresthesia, dysgeusia, cardiac dysrhythmias, tremors, and tinnitus.
The drugs used for epidurals can also have side effects on the patient. The opioids commonly used can cause nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression, decreased levels of consciousness, and the excessive itchiness all over the body.
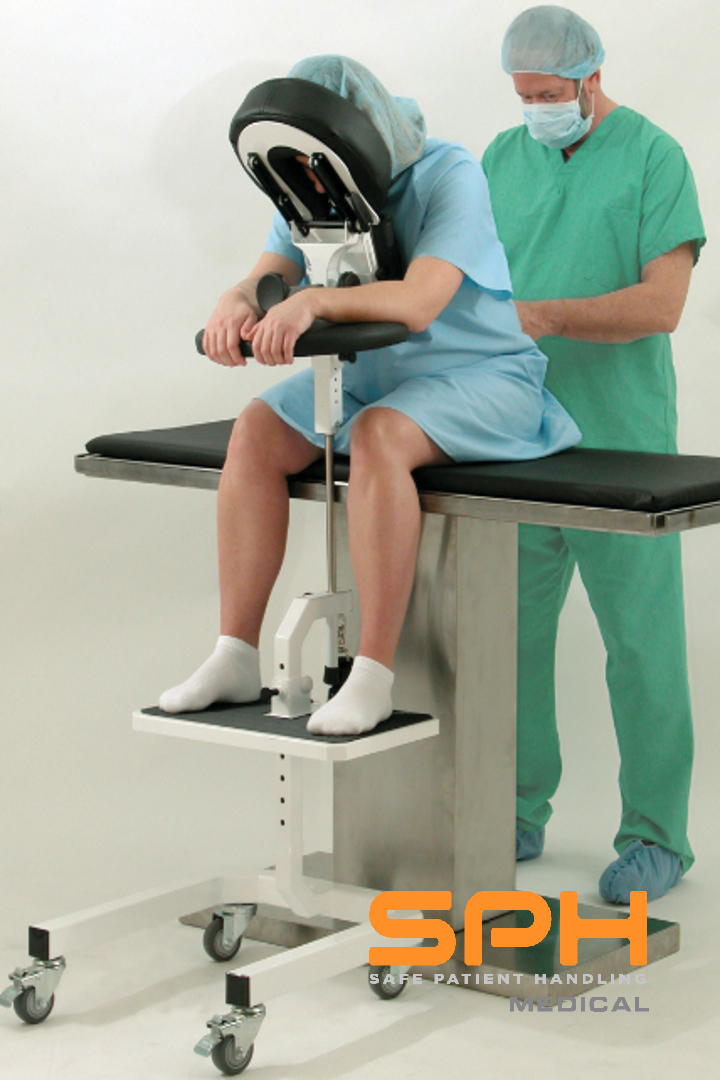
Nurses and medical personnel are at risk for getting injuries when administering epidurals as well. Positioning the patient correctly and supporting them while administering the epidural can be a potentially dangerous task. This has typically been a manual process of holding and supporting the patient. Manual patient handling is the cause of many back injuries for nurses across the country as well as strains and sprains. Musculoskeletal Disorders The Epidural Positioning Device is a key tool to keep the patient and doctor safe. It assists patients with maintaining the optimal position for their epidural to be administered. This is because it supports cervical, thoracic, and lumbar flexion. This positioning is essential because a patient can be paralyzed if they were to slip out of position while the needle was injected. The chair prevents doctors and staff from straining as well. It also allows patients more personal space, as opposed to traditional methods of epidural safety administration.