Solving Lateral Transfer and Positioning Risk in Hospitals
A Lateral transfer and patient repositioning are typical tasks of nursing staff around the globe. In fact, it’s estimated by the American Nursing Association that the average nurse moves around 1.8 tons during a full eight-hour shift. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, this immense amount of movement has resulted in medical professionals being at a 31.1 percent increased risk of musculoskeletal disorders.
The Federal Government has noted the increased workplace harm that those in the medical industry undergo due to lateral transfer and repositioning injury. In 2015, the national government passed new legislation regarding patient handling in the form of the Nurse and Health Care Worker Protection Act. This Act is geared towards shifting healthcare facilities into creating a safer workplace environment for caregivers.
The Biggest Problems With Lateral Transfers
A traditional lateral transfer is performed hundreds of times a day throughout all hospital departments, including ICU, imaging, emergency, surgery, and other medical units. Total care patients are unable to move their body weight from one surface to another. This situation results in the nursing staff physically moving the patient.
This move is performed in one of two ways. With the first method, the nursing staff grabs ahold of a sheet that is positioned underneath the patient. All staff members lift up on the draw sheet and physically lift the patient to another surface. In cases where fewer staff members are present, nurses use a plastic board and pull the draw sheet underneath the patient onto the other surface.
Both of these methods require a great deal of movement and strength from the nursing staff. This typically results in nursing injury in the form of back pain. With so many medical staffers undergoing musculoskeletal injuries, it has become clear that manual patient handling tasks need to be replaced with more efficient methods.
The Introduction of Air Powered Transfer Equipment
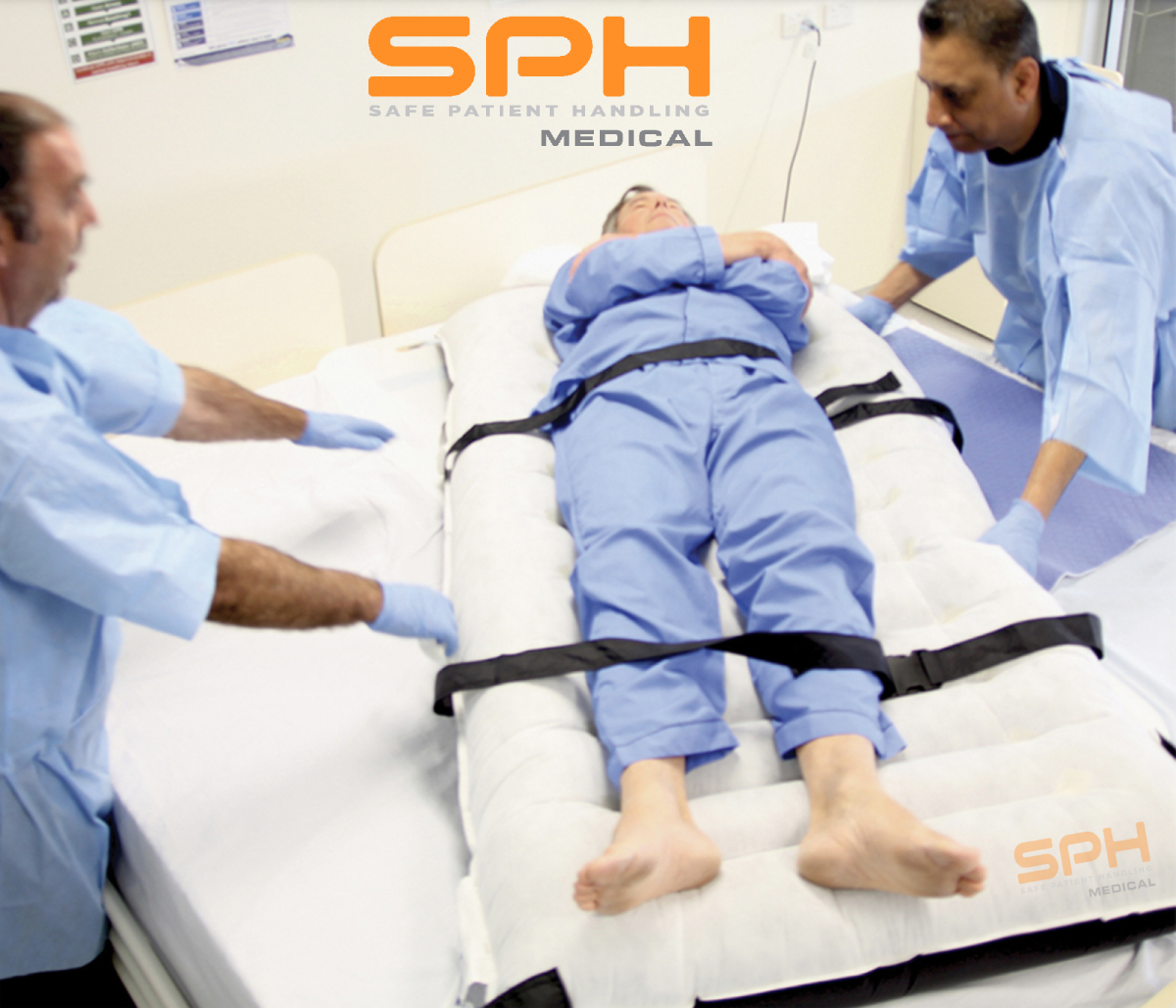
In recent years, companies like hovermatt and others have introduced air powered transfer technology. These transfer systems use a thin cushion of air under a mattress that is inflated. This system works to reduce friction and provides a floating action during patient lateral transfer.
These air powered transfer systems can be easily used for both lateral patient transfers and patient repositioning, also known as boosting a patient. The inflatable mattress transfer systems are intended to be left underneath the patient during their hospital stay.
A Look At The Many Benefits Of Air Powered Systems
It’s a wide concern of any medical facility to properly protect the long-term health of their staff. Lateral transfers and patient repositioning are well-known issues that create chronic health problems for medical staff members. Air powered systems have provided a quality solution that allows less manual labor on the part of a hospital’s medical staff. This works to reduce the overall risk of chronic injuries to caregivers.
When it comes to patients, air powered systems are providing a more comfortable and safer experience. Instead of being forcefully heaved from one surface to another under the manual power of medical staff, patients can be easily floated from one surface to the next. This makes the transferring and repositioning experience much smoother for patients.
In addition, air powered systems don’t require the patient to be lifted off of any surface. Rather, the inflatable mattress can be smoothly pulled from one surface to the next. This makes the lateral transfer experience much safer for the patient as there is less risk of bumps, bruises, or manual handling during transfers.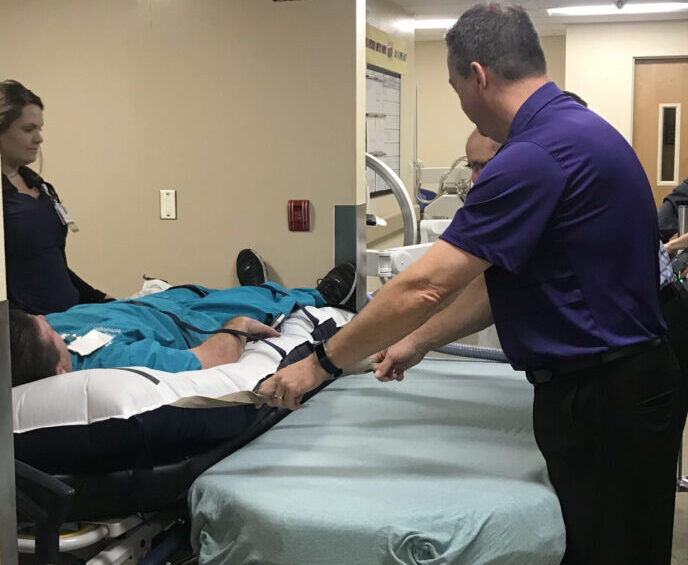
Air powered systems are tremendously changing the way that medical staffers perform repositioning and lateral transfers throughout their day. These systems drastically reduce the amount of strain that is placed on the nursing staff. From a patients perspective, they provide a safer and more comfortable experience for patients.



